Welcome back to TechCrunch Mobility — your central hub for news and insights on the future of transportation. To get this in your inbox, sign up here for free — just click TechCrunch Mobility!
A quick bit of breaking news that hit just as…

Welcome back to TechCrunch Mobility — your central hub for news and insights on the future of transportation. To get this in your inbox, sign up here for free — just click TechCrunch Mobility!
A quick bit of breaking news that hit just as…
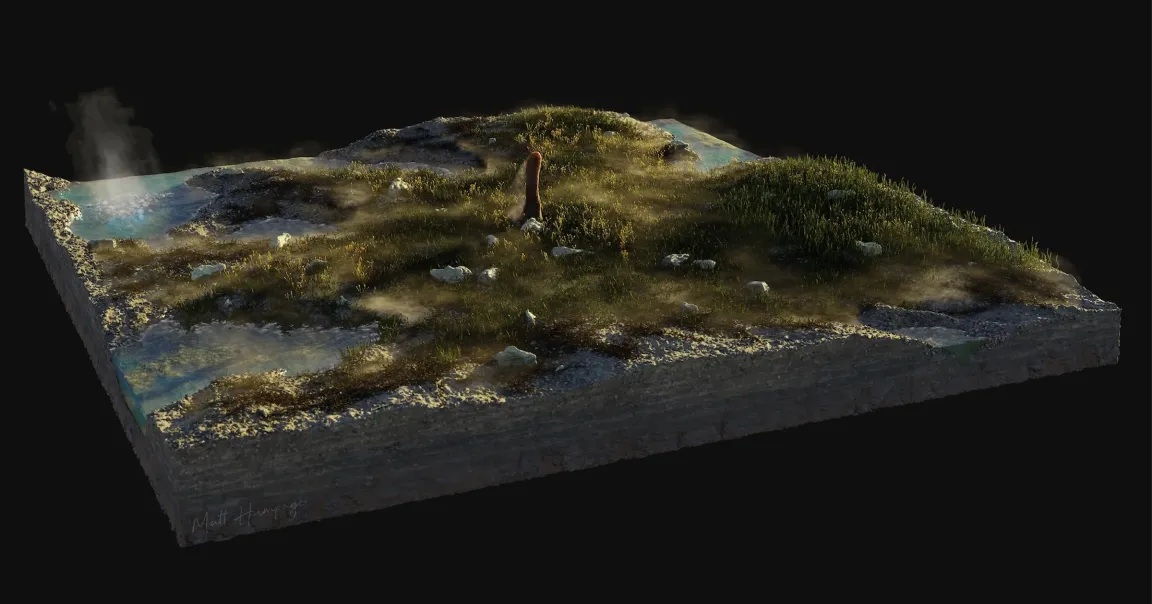
It’s a plant! It’s a fungus! It’s… an entirely new type of lifeform hitherto unknown to science?
That appears to be the case for a…
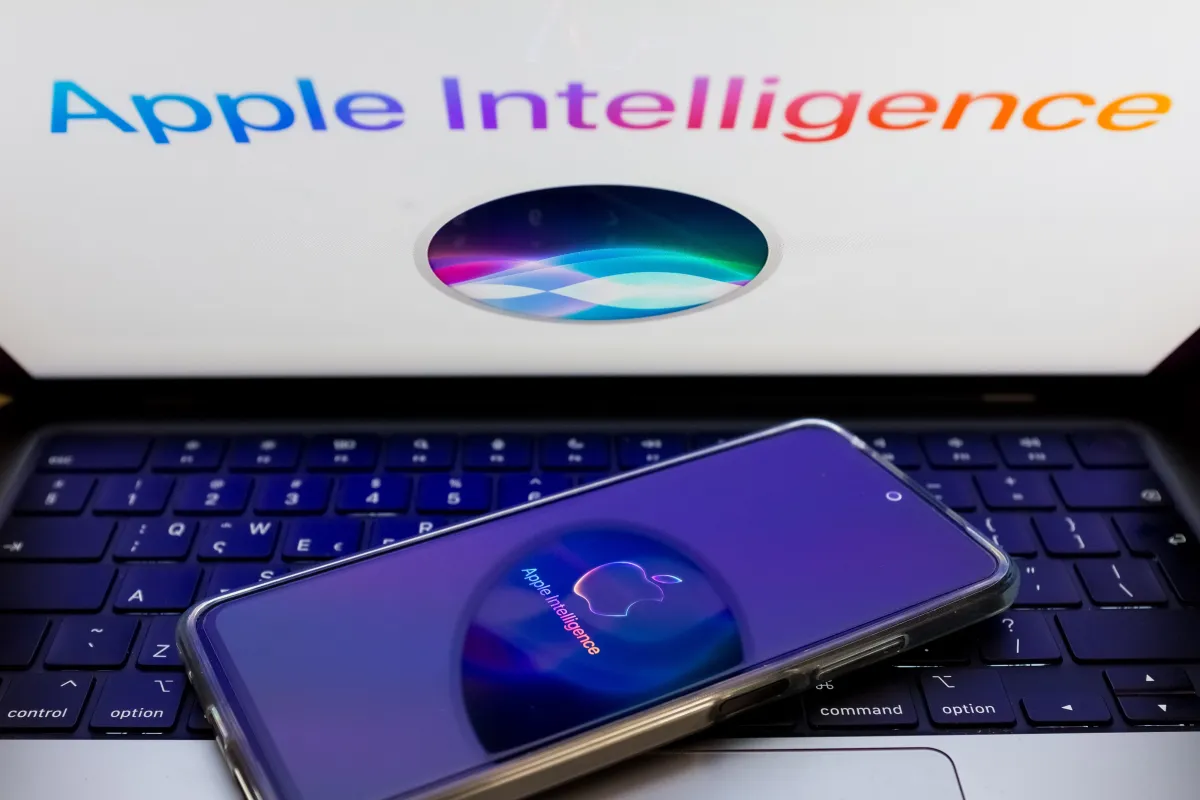

We’re about to get our first real look at the results of the recently announced AI partnership between Apple and Google, according to Bloomberg’s Mark Gurman.
Gurman reports that Apple is planning to announce a new version of Siri in the…
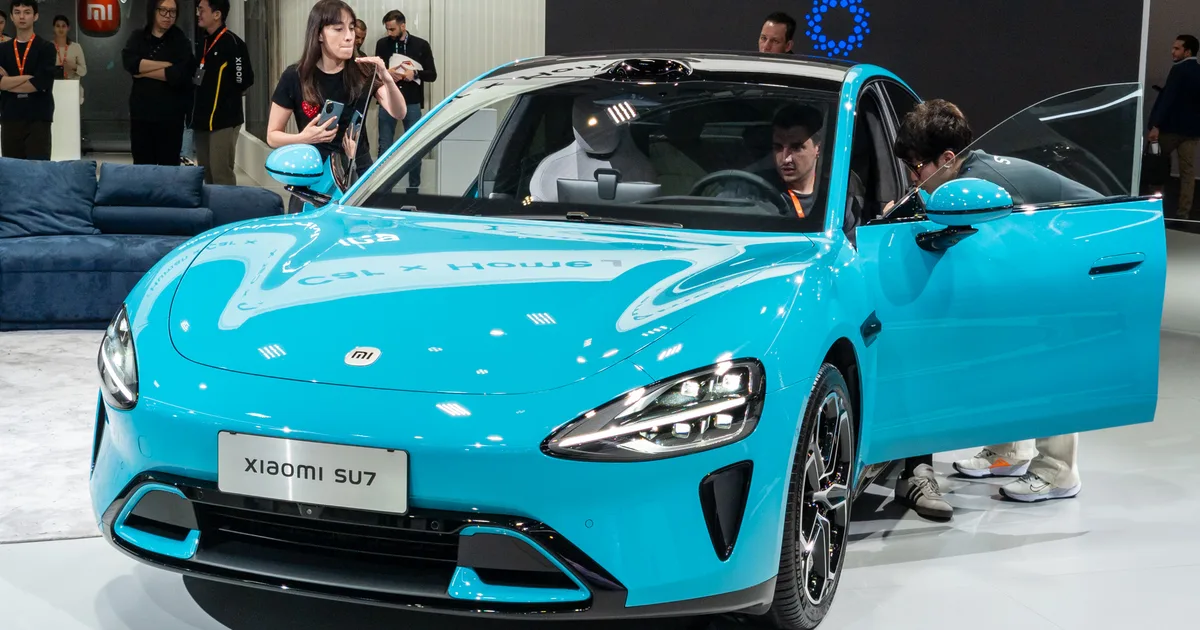

In what is one of the most important developments in the Chinese auto industry, Xiaomi’s SU7 has outsold Tesla’s Model 3 in 2025. The information comes from the China Passenger Car Association (via scmp.com).
The Chinese smartphone…
Global food trade is essential for food security, but its ecological consequences often remain unseen. A new data paper published in One Ecosystem introduces a global long-term dataset, quantifying biodiversity loss embodied in the international…
Researchers from Monash University and the Lions Eye Institute have discovered a tissue protein that acts as a central ‘traffic controller’ for immune cells and can be hijacked by a virus to weaken immune responses.
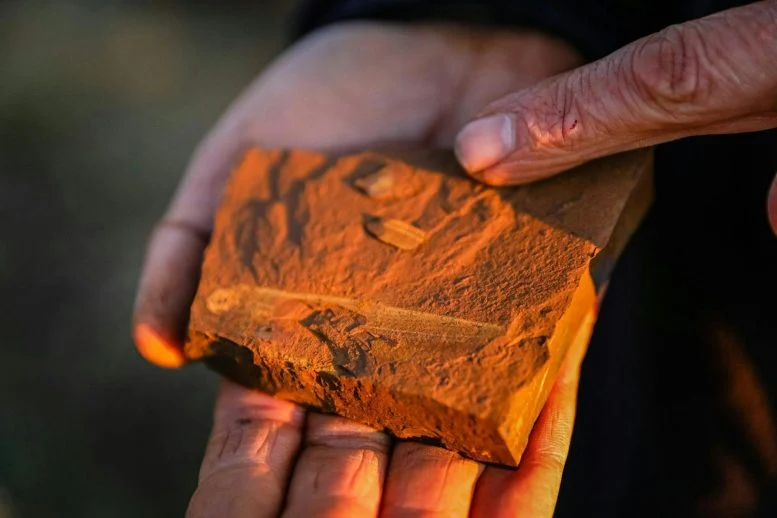

Iron-rich rocks at McGraths Flat preserve Miocene rainforest life in remarkable detail, reshaping ideas about how and where exceptional fossils form. Beneath agricultural land in the central tablelands of New South Wales sits one of Australia’s…

Scientists from A*STAR Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology (A*STAR IMCB) have identified why certain lung cancer cells become highly resistant to treatment after developing mutations in a key gene called EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor).

Quantum computers, systems that process information leveraging quantum mechanical effects, will require faster and energy-efficient memory components, which will allow them to perform well on complex tasks. Superconducting memories are promising…

“Hearst Magazines and Yahoo may earn commission or revenue on some items through these links.”
Here’s what you’ll learn when you read this story:
The human eye does not actually see purple, as purple is not a color on the visual spectrum.
Purple…