Kumbhakar, P. et al. Prospective applications of two-dimensional materials beyond laboratory frontiers: A review. iScience 26, 106671 (2023).
Ahn, E. C. 2D materials for spintronic devices. npj 2D Mater. Appl. 4, 17 (2020).
…
Kumbhakar, P. et al. Prospective applications of two-dimensional materials beyond laboratory frontiers: A review. iScience 26, 106671 (2023).
Ahn, E. C. 2D materials for spintronic devices. npj 2D Mater. Appl. 4, 17 (2020).
…
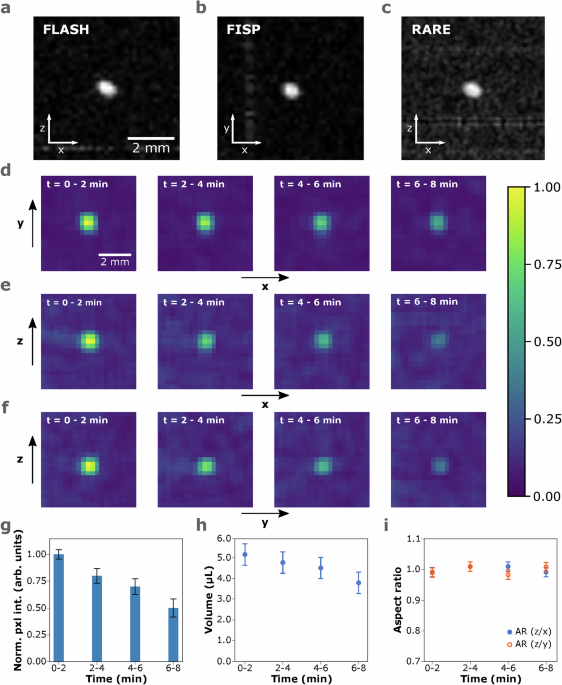
The design of the acoustic levitator was optimized22, and consisted of 18 × 2 demagnetized, ultrasonic transducers, positioned in a hexagonal arrangement. The levitator presented high acoustic levitation forces and…

To learn more about the nature of matter, energy, space, and time, physicists smash high-energy particles together in large accelerator machines, creating sprays of millions of particles per second of a variety of masses and speeds. The…
• Physics 18, s55
Simulations show that polymers that include inert and self-propelled components are more likely to form and retain knots, with possible applications in materials engineering.
Long molecules can become…
• Physics 18, s52
Fish swimming in vertical diamond formations gain efficiency through hydrodynamic interactions.
Fish travel in schools to defend against predators, improve navigation, and increase opportunities for…
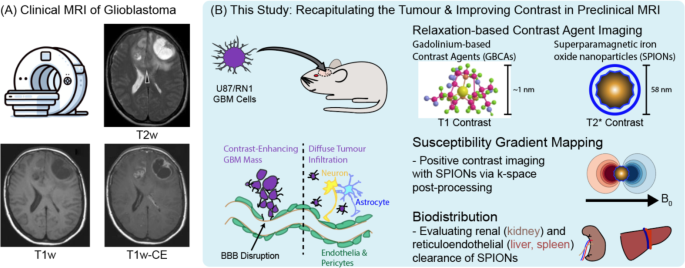
The nanoparticles evaluated in this study are novel magnetite(Fe3O4)-based, methoxy-PEG-coated SPIONs28. PEG-SPIONs (mPEG PrecisionMRX) were sourced commercially and received in aqueous solutions with elemental iron concentrations…
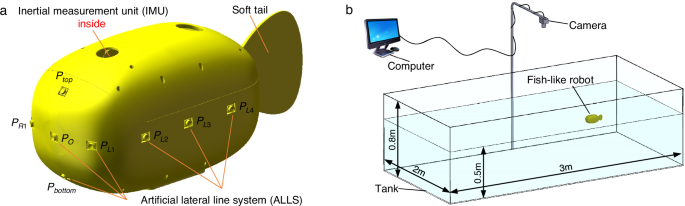
The fish-like robot (Fig. 1a and detailed in the “Methods” section) is inspired by boxfish (Ostracion cubicum) in nature. Its density is slightly less than one so that almost the entire body is submerged below…
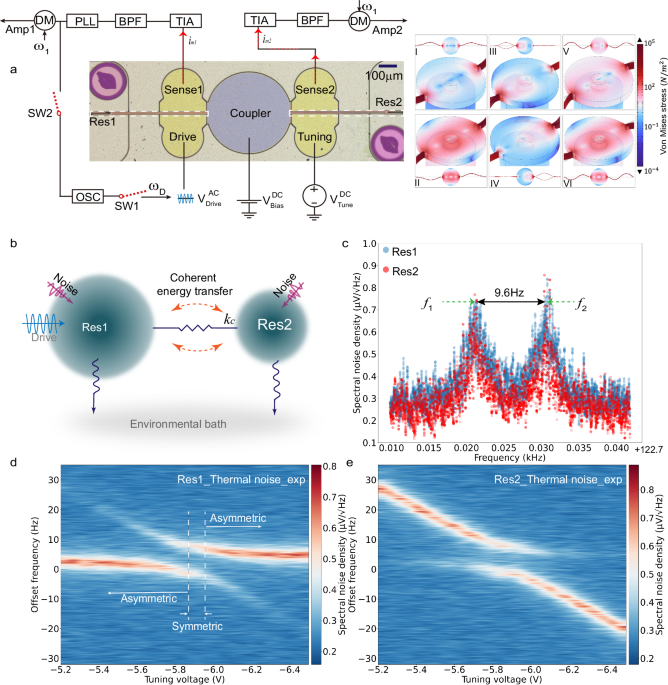
The proposed coupled micromechanical resonators system (Fig. 1a) was constructed with two double-ended-tuning-fork (DETF) resonators connected via a mechanical disc coupler anchored at the…
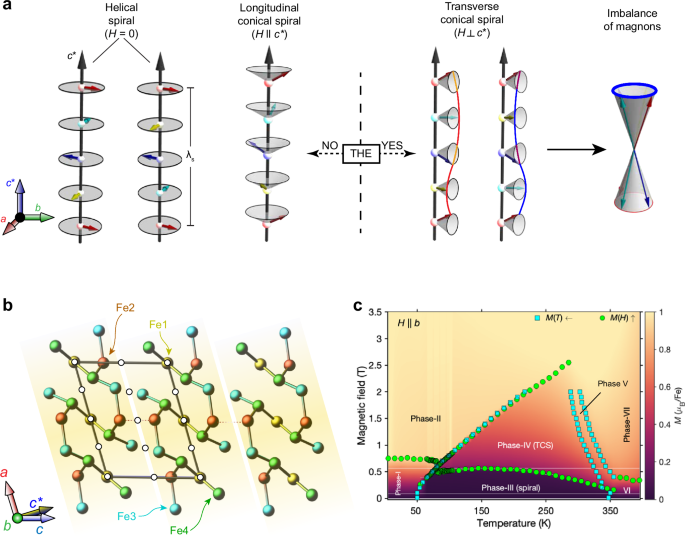
Our target material crystallises in a centrosymmetric structure shown in Fig. 1b with the monoclinic unit cell (C2/m, a = 10.0966(5) Å, b = 7.6650(4)…
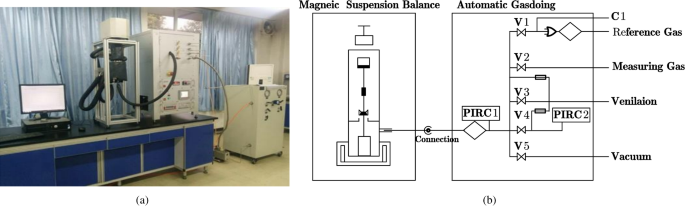
The experimental results showed that the adsorption and desorption curves do not overlap, with the desorption curve lying above the adsorption curve. This phenomenon can be attributed to the hysteresis…