Sagdeev, R. Z. Cooperative phenomena and shock waves in collisionless plasmas. In Reviews of Plasma Phys., Vol. 4 (ed. Leontovich, M. A.) 23–91 (Consultants Bureau, 1966).
Washimi, H. & Taniuti, T. Propagation of ion-acoustic solitary waves of…
Sagdeev, R. Z. Cooperative phenomena and shock waves in collisionless plasmas. In Reviews of Plasma Phys., Vol. 4 (ed. Leontovich, M. A.) 23–91 (Consultants Bureau, 1966).
Washimi, H. & Taniuti, T. Propagation of ion-acoustic solitary waves of…
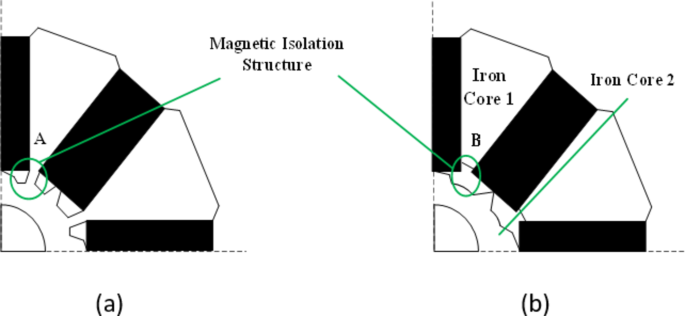
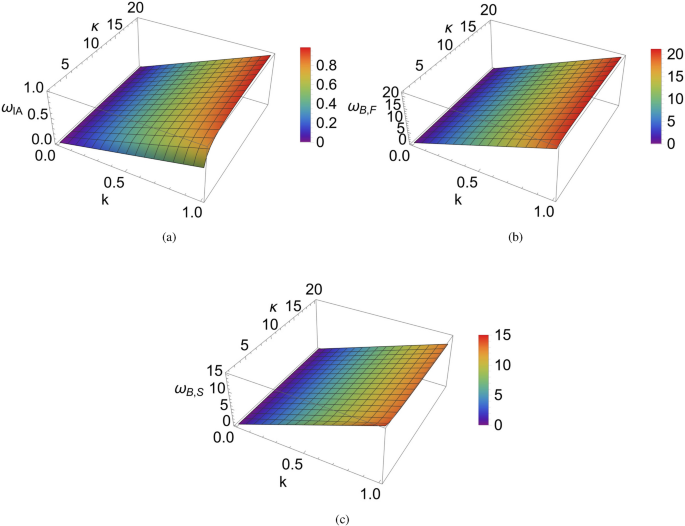
Hybrid vehicle oil pump motors commonly employ permanent magnet brushless DC motors. Due to the presence of rotor permanent magnets, it inevitably generates cogging torque, which seriously affects the low-speed performance of the motor19….
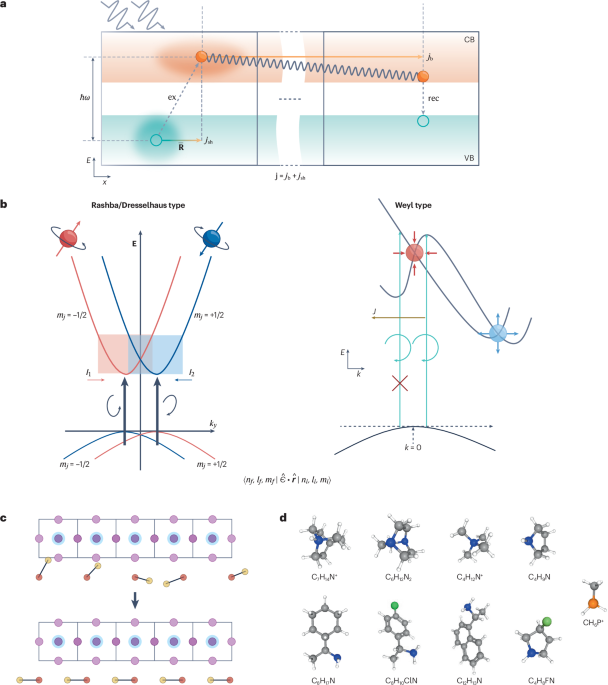
Stranks, S. D. et al. Electron–hole diffusion lengths exceeding 1 micrometer in an organometal trihalide perovskite absorber. Science 342, 341–344 (2013).
Google Scholar
Huang,…
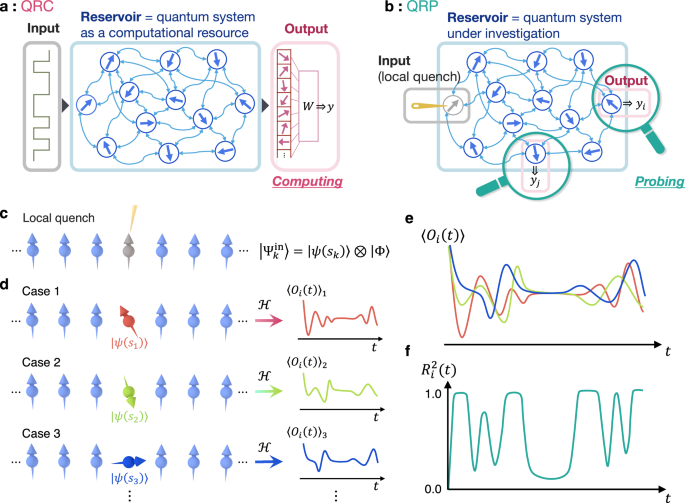
Before going to the QRP, we provide an overview of a brain-inspired machine-learning framework called reservoir computing36,37,38. In this paradigm, information is nonlinearly processed by networks of artificial neurons,…

To learn more about the nature of matter, energy, space, and time, physicists smash high-energy particles together in large accelerator machines, creating sprays of millions of particles per second of a variety of masses and speeds. The…
• Physics 18, s55
Simulations show that polymers that include inert and self-propelled components are more likely to form and retain knots, with possible applications in materials engineering.
Long molecules can become…
• Physics 18, s52
Fish swimming in vertical diamond formations gain efficiency through hydrodynamic interactions.
Fish travel in schools to defend against predators, improve navigation, and increase opportunities for…
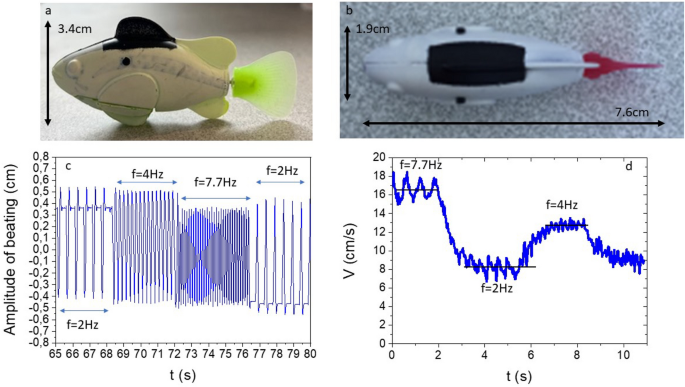
The fish robots: Photos of the toy fish (a) side view, (b) top view. (c) Beating amplitude versus time: three frequencies are apparent with the smallest one showing beating in one direction or the other (half duty cycle). (d) Velocity…
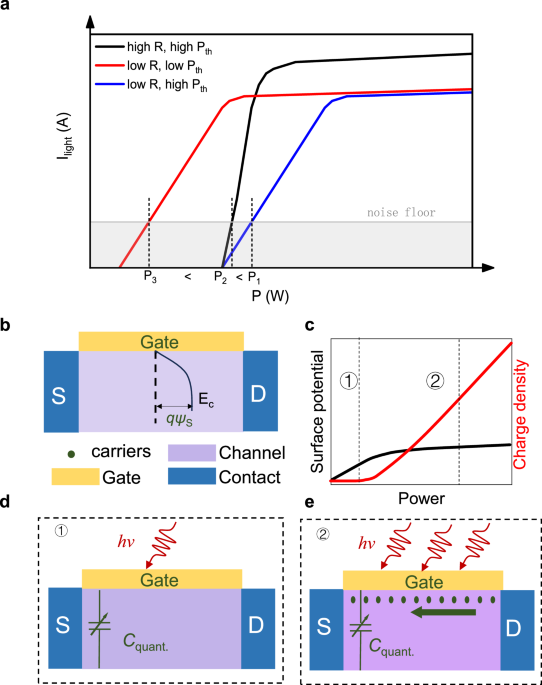
To examine our argument, we begin by analyzing the working mechanism for a semiconductor phototransistor/diode. This kind of device is the most commonly used photodetector, It mainly contains a semiconductor (e.g., p-n or p-i-n) junction7 (It…
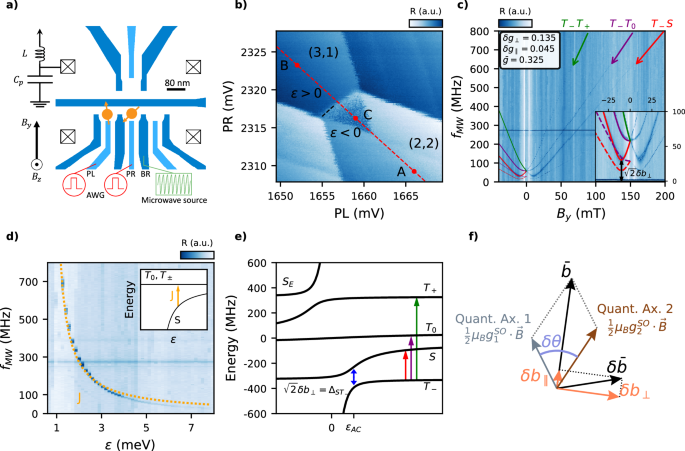
The schematics of the device used in the experiment is shown in Fig. 1a. Electrostatic gates deplete the two-dimensional hole gas beneath, creating a double quantum dot (DQD) on the bottom part of the device to be operated as a qubit. A single…