Learning time-local master equations by maximum-likelihood estimation
The Lindblad master equation generalizes the Schrödinger equation to open and noisy quantum systems74,78,79, and describes the non-unitary time evolution of the density matrix…
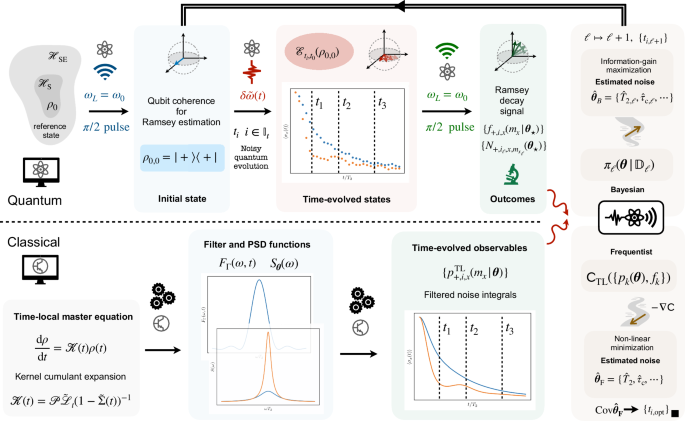
The Lindblad master equation generalizes the Schrödinger equation to open and noisy quantum systems74,78,79, and describes the non-unitary time evolution of the density matrix…
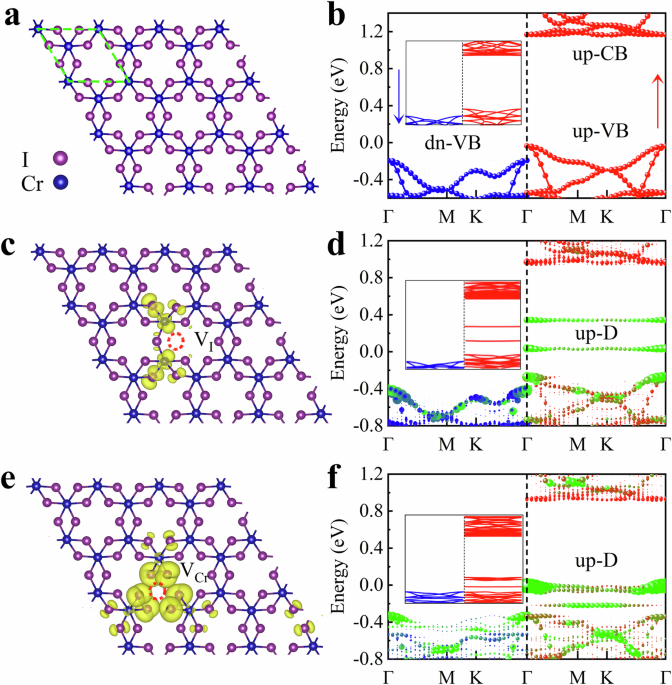
Investigating the electronic structures of both defective and pristine CrI3 systems is essential for understanding the SOC effects induced by defects on magnetic recovery dynamics (see electronic…
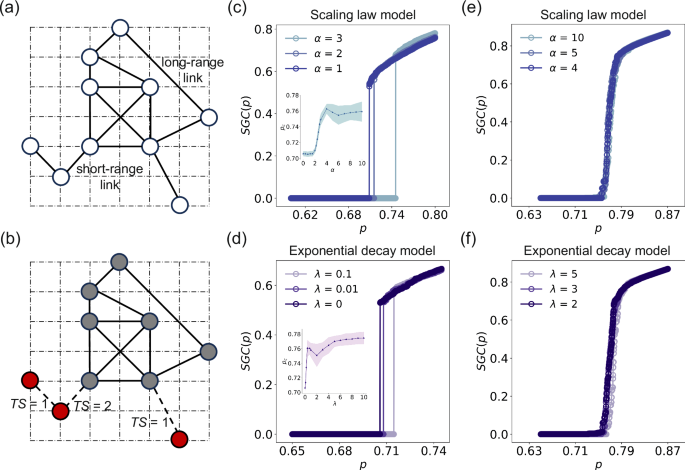
The spatial model employed is designed to generate networks with specific spatial connectivity patterns, where the likelihood of connections between nodes is determined by…
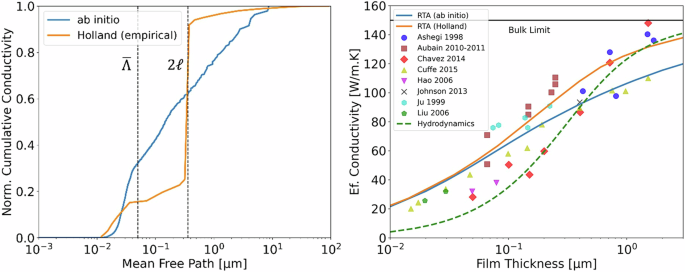
Warzoha, R. J. et al. Applications and impacts of nanoscale thermal transport in electronics packaging. J. Electron. Packag. Trans. ASME 143, 020804 (2021).
Google Scholar
Choi, S., Heller, E. R.,…
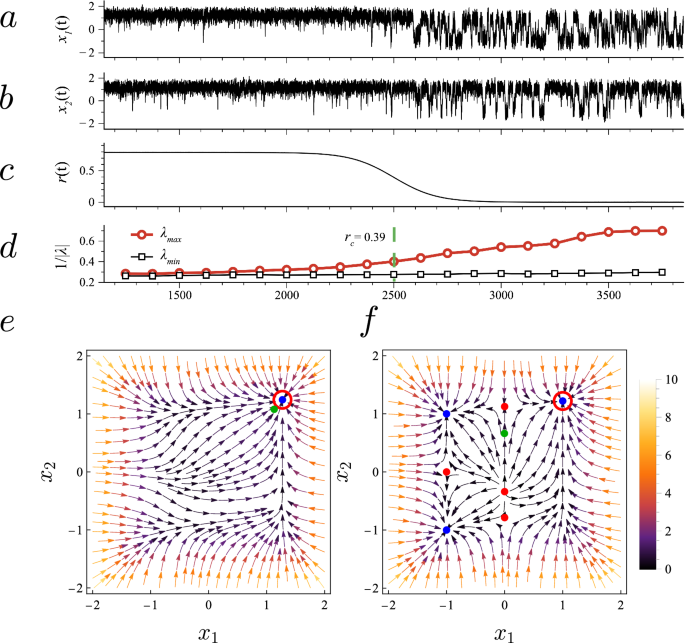
To validate our approach, we simulate time series from two- and ten-dimensional nonlinear systems with known dynamics and show that the estimated…
• Physics 18, s56
Liquid crystals can be coaxed into hosting an easily reconfigurable lattice of vortices useful for information encoding.
Some topological systems are attractive thanks to their resilience and ability to…
• Physics 18, 115
The harsh interstellar environment ought to destroy these carbon-rich molecules; experiments reveal their secret weapon.
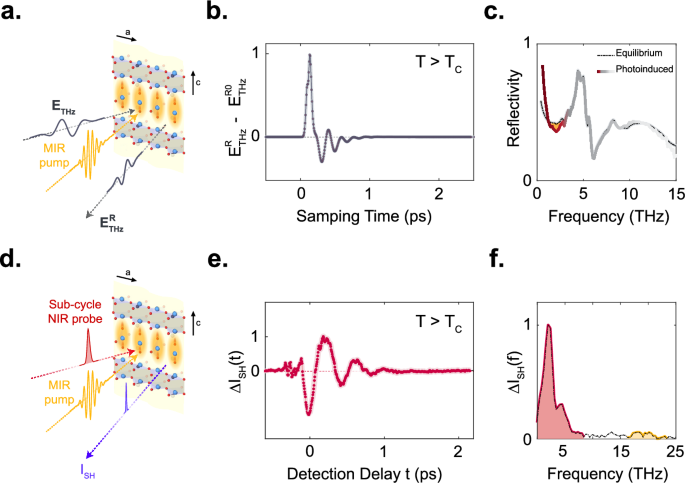
The coherent, time delay dependent oscillations in \(\varDelta {I}_{{SH}}\) induced by an infrared-active mode \({Q}_{i}({\omega }_{i})\) of a solid at frequency \({\omega }_{i}\) can be cast in the…
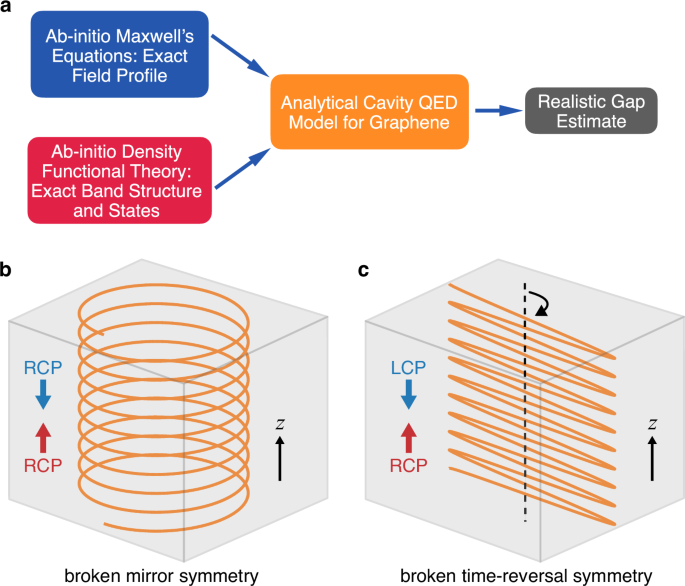
Here, we provide a concise overview of the distinction between chiral cavities with broken mirror symmetry and those with broken TRS. Chiral matter exhibits different optical responses to LCP and RCP light….
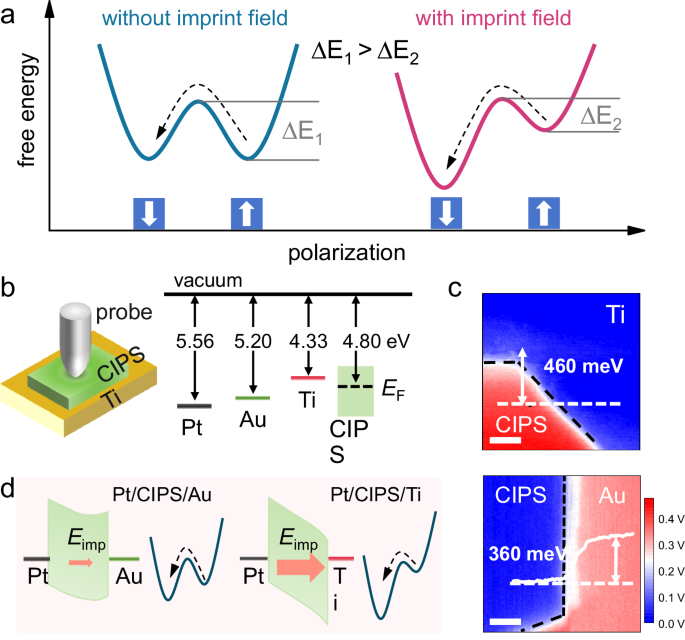
We first explain the strategy for enabling low-force polarization switching by introducing an imprint field via asymmetric electrostatic boundary conditions in ferroelectric materials. As known, the…