By utilizing Eq.(3) into the Eq.(1) with \(h_{1}=0,\) we achieve
$$\begin{aligned} \left\{ \begin{array}{c} \omega M^{^{\prime \prime }}-MN^{^{\prime }}=0, \\ \omega N^{^{\prime \prime }}+MM^{^{\prime }}=0. \end{array} \right. \end{aligned}$$
…
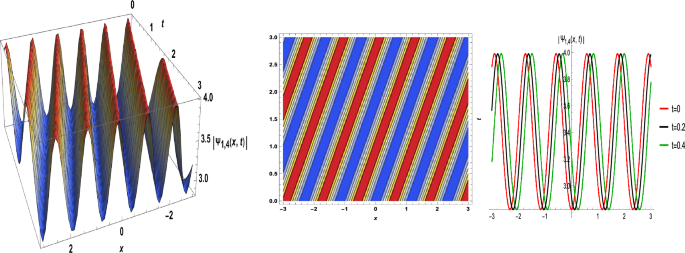
By utilizing Eq.(3) into the Eq.(1) with \(h_{1}=0,\) we achieve
$$\begin{aligned} \left\{ \begin{array}{c} \omega M^{^{\prime \prime }}-MN^{^{\prime }}=0, \\ \omega N^{^{\prime \prime }}+MM^{^{\prime }}=0. \end{array} \right. \end{aligned}$$
…

Kitaev, A. Anyons in an exactly solved model and beyond. Ann. Phys. 321, 2–111 (2006).
Google Scholar
Kitaev, A. Y. Fault-tolerant quantum computation by anyons. Ann. Phys. 303, 2–30…

Sulfur compounds like hydrogen sulfide, methyl mercaptan, ethyl mercaptan, and thionyl carbon pose safety risks1,2, induce pipeline corrosion, and impacting on natural gas quality. Consequently, monitoring these compounds throughout the stages of…

Consider M-mode linear-optical circuits with N single-photon inputs and arbitrary local measurements. Linear-optical circuits consist of beam-splitter layers, which may be geometrically non-local, i.e.,…

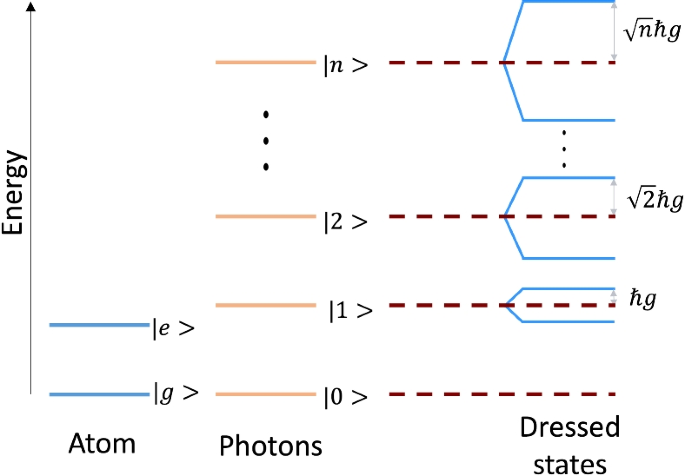
We use the Generalized Holstein-Tavis-Cummings (GHTC) Hamiltonian23,24,25,26 to describe N excitons interacting with \({{{\mathcal{M}}}}\) cavity modes, and \(N\gg {{{\mathcal{M}}}}\) in line with typical experimental conditions….

The cavity length is defined by the 4f requirement to be \(\sim 30\,\text {cm}\). Accounting for the optical path length differences introduced by the lenses results in an actual length of approximately \(30.6\,\text {cm}\). This…
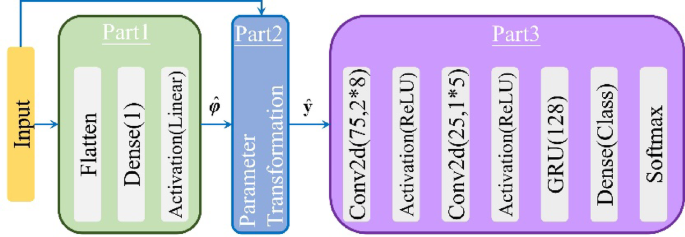
The proposed Parameter Estimation and Transformation-based CNN-GRU Deep Neural Network (PET-CGDNN) model consists of a parameter estimator, a parameter transformer, and a hybrid neural network, as depicted in Fig. 1.
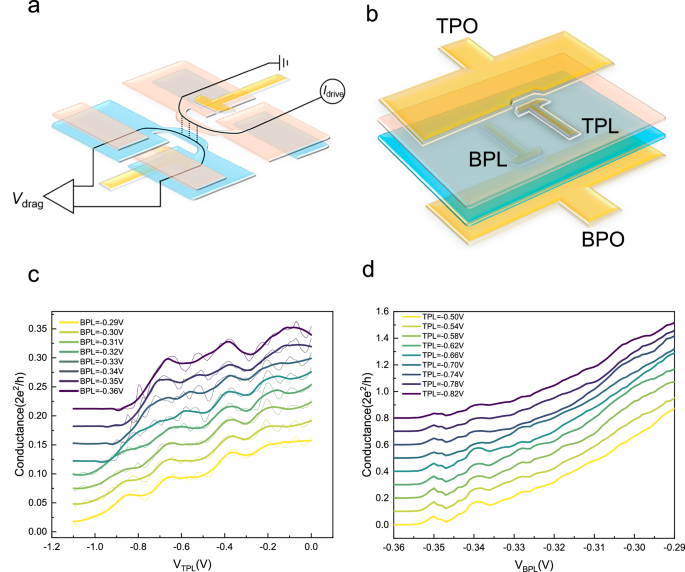
A schematic of the vertically-coupled quantum wires devices used in this work is shown in Fig. 1b, with a typical optical image provided (see Supplementary Fig. 1). As the two wires are defined in two…
Wang, X., Zhao, Y. & Pourpanah, F. Recent advances in deep learning. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybernet. 11, 747–750 (2020).
Young, T., Hazarika, D., Poria, S. & Cambria, E. Recent trends in deep…
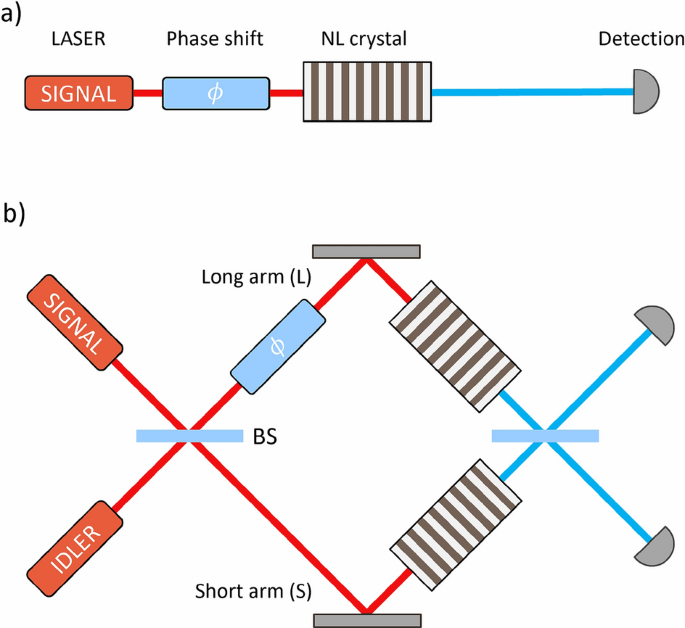
Super-resolution can be explained via the definition of maximally entangled state, that can be written as25:
$$\begin{aligned} |\psi \rangle = \frac{|N,0\rangle _{ab} + e^{iN\phi }|0,N\rangle _{ab}}{\sqrt{2}}\,. \end{aligned}$$
…