Ergun, S. & Alexander, L. E. Crystalline forms of carbon: a possible hexagonal polymorph of diamond. Nature 195, 765–767 (1962).
Google Scholar
E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company….

Ergun, S. & Alexander, L. E. Crystalline forms of carbon: a possible hexagonal polymorph of diamond. Nature 195, 765–767 (1962).
Google Scholar
E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company….

Laser beams programmed to form various shapes by nanodisk arrays
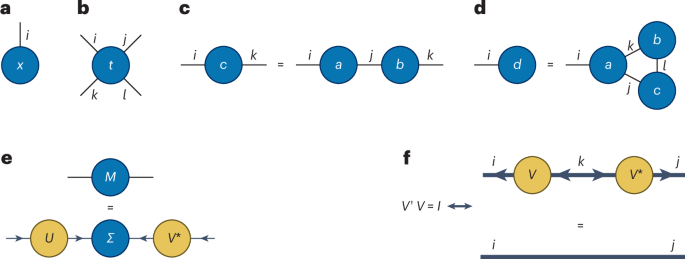
Schollwöck, U. The density-matrix renormalization group in the age of matrix product states. Ann. Phys. 326, 96–192 (2011).
Google Scholar
Orús, R. Tensor networks for complex…
The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is tough on electronics. Situated inside a 17-mile-long tunnel that runs in a circle under the border between Switzerland and France, this massive scientific instrument accelerates particles close to the speed of…
• Physics 18, s100
A laser-plasma-driven free-electron laser achieves record performance, marking a step toward making intense, ultrafast x-ray sources more accessible.
T. Swift/LBNL
For two decades,…

In a fascinating dive into the strange world of quantum physics, scientists have shown that light can interact with itself in bizarre ways—creating ghost-like virtual particles that pop in and out of existence. This “light-on-light scattering”…
MIT physicists have performed the most precise version of the famous double-slit experiment, using ultracold atoms and single photons to reveal the strange dual nature of light as both wave and particle. This quantum balancing act—long debated…

Gold remains perfectly solid when briefly heated beyond previously hypothesized limits, a new study reports, which may mean a complete reevaluation of how matter behaves under extreme conditions.
The international team of scientists behind the…
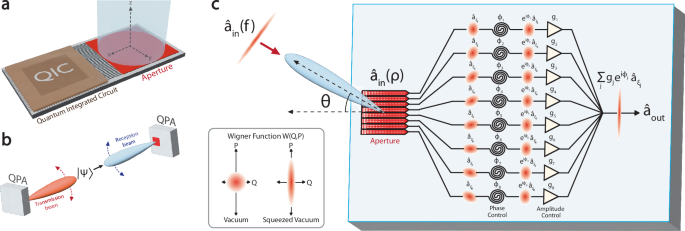
Consider a quantized electromagnetic field \(\hat{E}\) transmitted over free space to a phased array receiver. The field can be decomposed into positive and negative frequency components, \(\hat{E}={\hat{E}}^{+}+{\hat{E}}^{-}\), where
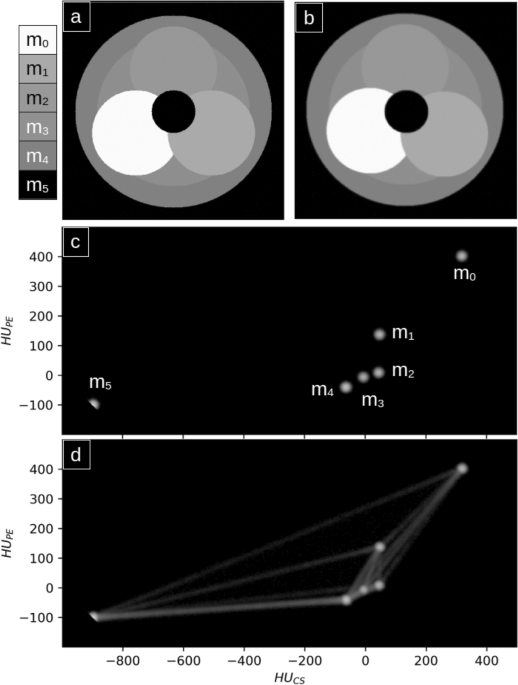
In 1976 Alvarez and Macovski14 described that for energies relevant for medical imaging, the x-ray attenuation \(\mu\) for any material can be approximated as
$$\begin{aligned} \mu (Z,E) = a_{PE}(Z) \times…