Microwave treatment mechanism
The interaction was based on the scientific theory that microwave radiation has high selectivity, and this selectivity depends on the dipole moment of the materials exposed to it. Furthermore, numerous investigations…
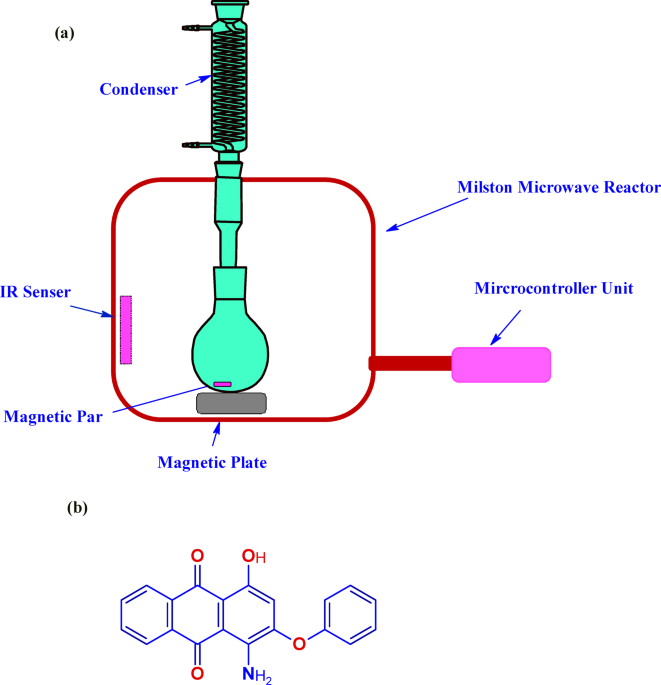
The interaction was based on the scientific theory that microwave radiation has high selectivity, and this selectivity depends on the dipole moment of the materials exposed to it. Furthermore, numerous investigations…
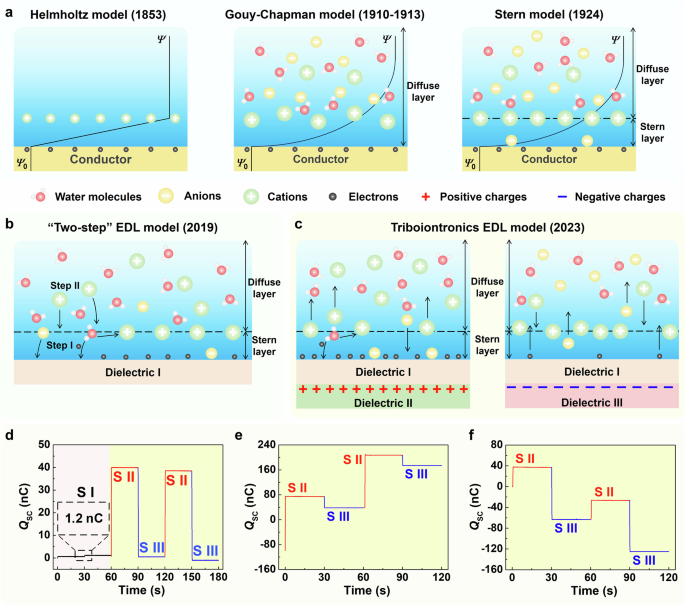
By dynamically regulating the EDL to modulate interfacial charge behavior, a robust framework can be established for emulating biological neural signal transmission, thereby enabling the construction of neuromimetic circuits for efficient…
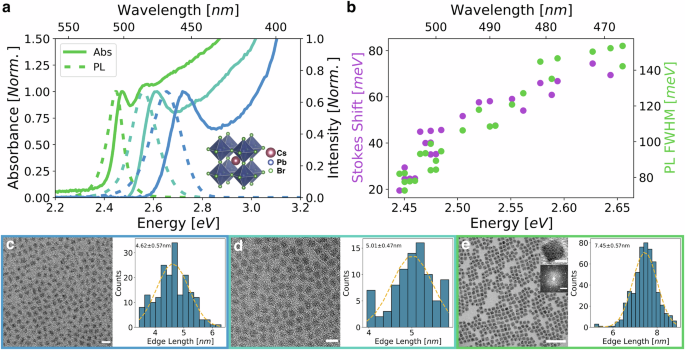
We investigated the effect of nanocrystal size on optical properties, focusing on the radiative lifetime. Over 30 high-quality nanocrystals samples were synthesized following a modified version of previous reports (details in the Method section)…
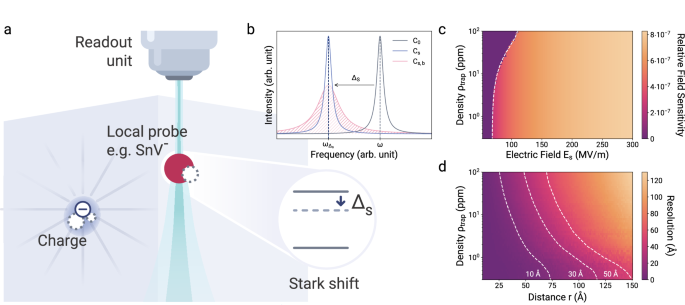
Here, we provide an overview of the general methodology of simulating single and multimodal spectra (Fig. 2b). The simulations begin with distributing charge traps uniformly within a specified volume or surface. For…
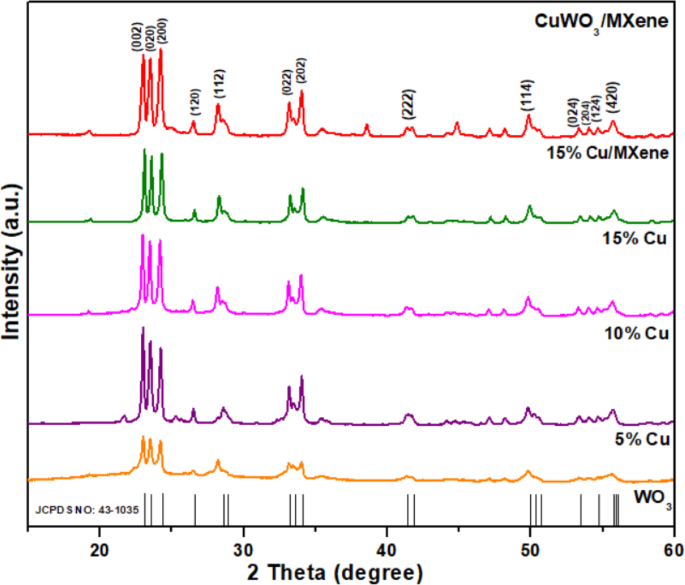
XRD spectra of Pure WO3, Cu-WO3 (Cu x% =5 at%, 10 at%, 15 at%) and 15 at% Cu-WO3/MXene nanocomposite.
By utilizing an XRD equipped with Cu Kα radiation as the source (λ ≈ 1.5406 Å), the material’s…
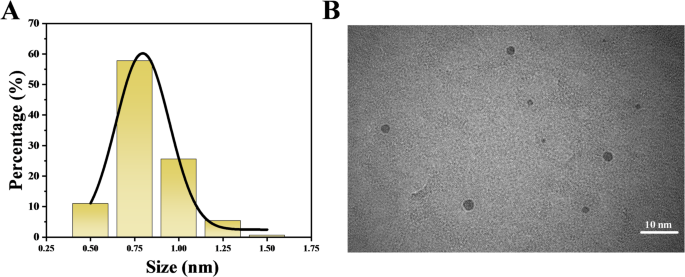
CDs’ morphology was observed by TEM imaging. The generated CDs seemed monodispersed and had a spherical shape, as observed in Fig. 1B. As shown in Fig. 1A, the size distribution of the CDs has…
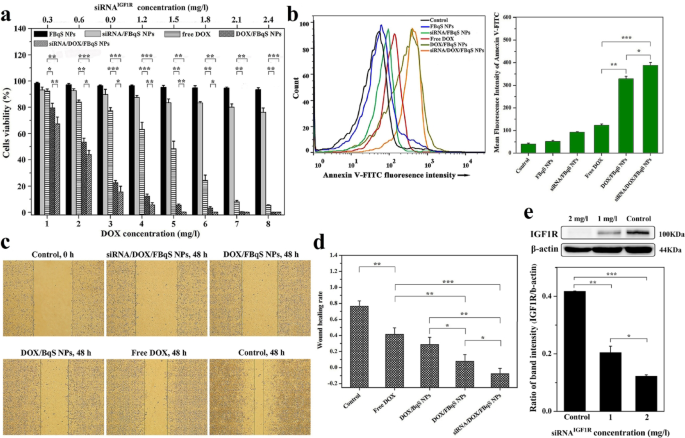
The blank, various drug-loaded biotin-quaternized starch nanoparticles (BqS NPs) and FBqS NPs in different drug concentrations were prepared according to our previous work26. All the other reagents used in this study…

A new nanocomposite membrane uses layered fiber design to combine strength, flexibility, and antibacterial function for improved bone regeneration.
These nanosheets operate using a dual-mode heat storage mechanism, where water molecules are simultaneously absorbed (intercalated) and adsorbed from the atmosphere.

A new ring-based tunable laser on a chip emits multiple wavelengths smoothly, offering a compact, cost-effective alternative for sensing, diagnostics, and more.