Glass embedded with electric-field-driven electrodes removes dust from its surface without water or scrubbing, offering a durable, passive cleaning solution for solar panels and other exposed optical systems.
Category: Nanotech
-

Self-cleaning glass uses electric fields to remove dust from its surface
-

Flexible silver nanowire film boosts infrared camera performance and visibility
Researchers create transparent silver nanowire electrodes to improve IR cameras, enabling clearer imaging and flexible designs for real-world applications.
Continue Reading
-
Flexible optoelectronics made efficient with low-temperature hydrogen process
Scientists developed flexible optoelectronic device using low-temperature process with minimized thin-film defects via hydrogen dilution control.
Continue Reading
-
Light-powered nano-motor enables mechanical synthesis of interlocked 3D molecules
Researchers used a light-driven molecular motor to wind two molecular strands into an interlocked ring structure called a catenane, without forming chemical bonds.
Continue Reading
-

Eco-friendly sensor enables rapid detection of pharmaceutical contaminants in water
Researchers developed a carbon nanofiber-based sensor that detects two drugs at once in water, offering a sensitive, low-cost, eco-friendly monitoring solution.
Continue Reading
-
Cool new imaging method of frozen solvents shows elemental distributions in nanomaterials
Researchers developed a cryo-EELS/EF-TEM method to map structure and elements of nanomaterials in frozen solvents with high resolution.
Continue Reading
-
Nanodevice uses sound to sculpt light, paving the way for better displays and imaging
Researchers have found a novel way to use high-frequency acoustic waves to mechanically manipulate light at the nanometer scale. Potential applications include everything from ultrathin screens to optimized holographic VR headsets.
Continue Reading
-
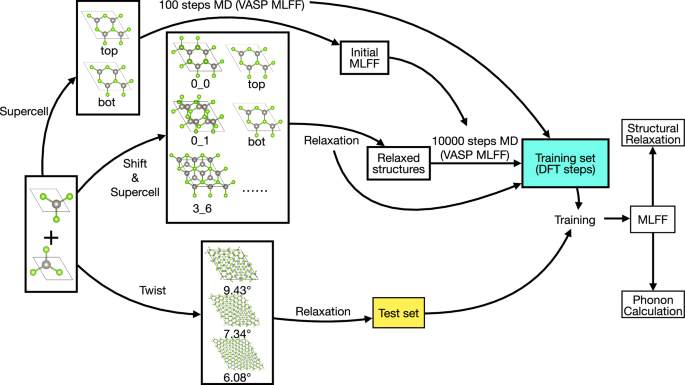
DPmoire: a tool for constructing accurate machine learning force fields in moiré systems
Cao, Y. et al. Unconventional superconductivity in magic-angle graphene superlattices. Nature 556, 43–50 (2018).
Google Scholar
Cao, Y. et al. Correlated insulator behaviour at half-filling in…
Continue Reading
-
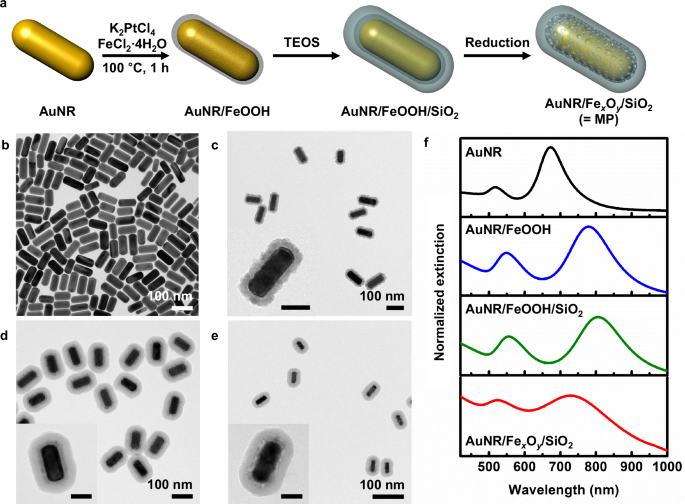
Dynamic birefringence and chirality of magnetically controllable assemblies of anisotropic plasmonic nanoparticles in dispersion
Materials
Gold(III) chloride trihydrate (HAuCl4·3H2O; ≥99.9%), CTAB (≥98%), sodium borohydride (NaBH4; 99%), trisodium citrate, silver nitrate (AgNO3; 99.9999%), L-ascorbic acid (reagent grade), CTAC (≥98%), citric acid (ACS reagent,…
Continue Reading
-
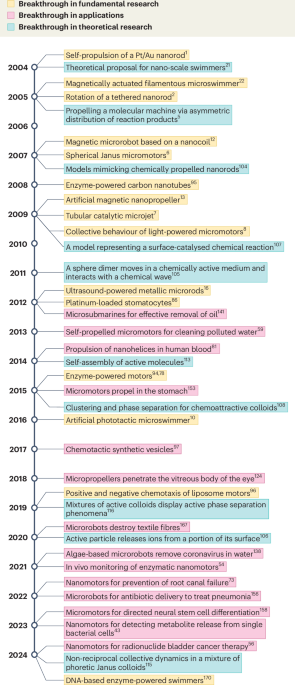
A roadmap for next-generation nanomotors
Paxton, W. F. et al. Catalytic nanomotors: autonomous movement of striped nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 13424–13431 (2004). A landmark study that introduced chemically powered nanomotors, launching the field of synthetic nanomotor research.
Continue Reading