This section provides a detailed description of the datasets utilized to evaluate the proposed method’s performance, specifying the metrics employed to assess its effectiveness and showcasing the results obtained from the implemented approach.
Category: 7. Maths
-
A deep learning framework for gender sensitive speech emotion recognition based on MFCC feature selection and SHAP analysis
To validate the presented approach, all stages were developed and simulated in MATLAB. This simulation displays the results of an emotion recognition algorithm applied to the speaker’s speech. It also enables the comparison of these results to…
Continue Reading
-
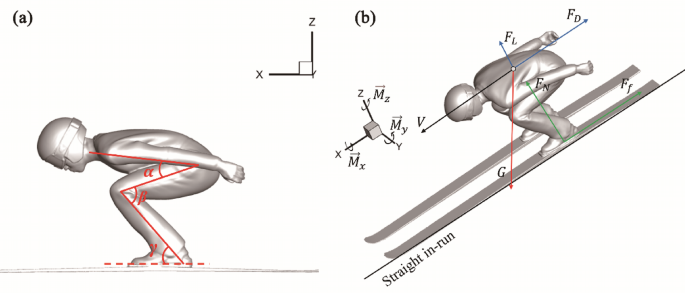
Numerical analysis of ski suits surface roughness effects on aerodynamics during the in-run phase of ski jumping
3D jumper models
To conduct aerodynamic simulations, a three-dimensional geometric model of the athlete–ski system during the straight-line descent of the in-run phase was established. The model was constructed using anthropometric data obtained…
Continue Reading
-

A note on the analysis of Herrmann–May lattices for small exponent RSA
In this section, we revisit the work of Herrmann et al.7, which focuses on maximizing small root bounds for RSA with a small secret exponent. In their approach, they introduced a novel technique known as the method of unravelled linearization….
Continue Reading
-
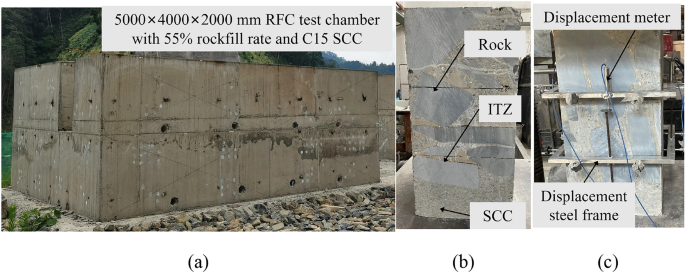
3D mesoscopic numerical investigation on the uniaxial compressive behavior of rock-filled concrete with different ITZ and aggregate properties
The mesoscopic scale is the state between macroscopic and microscopic, and its scale is generally between micrometers and millimeters. It has been shown that the RFC mesoscale range is in the millimeter level2,22,23. This section introduces a 3D…
Continue Reading
-

MIT tool visualizes and edits “physically impossible” objects | MIT News
M.C. Escher’s artwork is a gateway into a world of depth-defying optical illusions, featuring “impossible objects” that break the laws of physics with convoluted geometries. What you perceive his illustrations to be…
Continue Reading
-
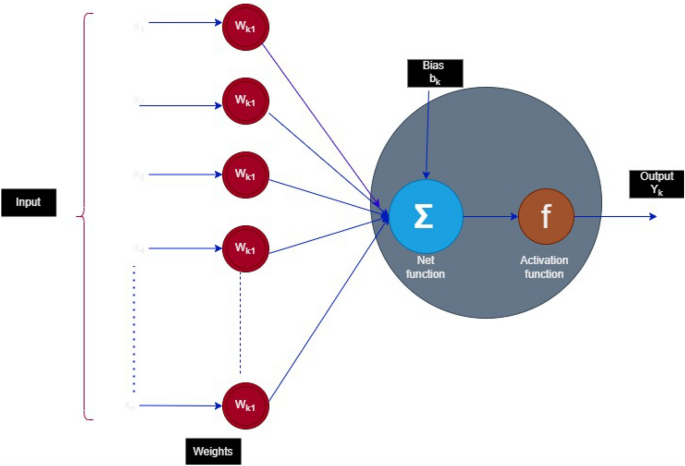
An intelligent framework for modeling nonlinear irreversible biochemical reactions using artificial neural networks
The numerical investigation of nonlinear irreversible biochemical reaction (NIBR) model is carried out using an advanced computational numerical solver called intelligent backpropagated by the Levenberg–Marquardt artificial neural networks…
Continue Reading
-
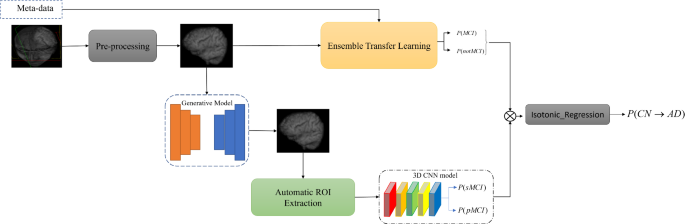
An integrated predictive model for Alzheimer’s disease progression from cognitively normal subjects using generated MRI and interpretable AI
CN to MCI progression
As we mentioned in the proposed method, the first phase of the proposed method is MCI progression prediction. In this phase, MRI images of the baseline as well as Demographic features (including Age, Gender, Marital Status,…
Continue Reading
-
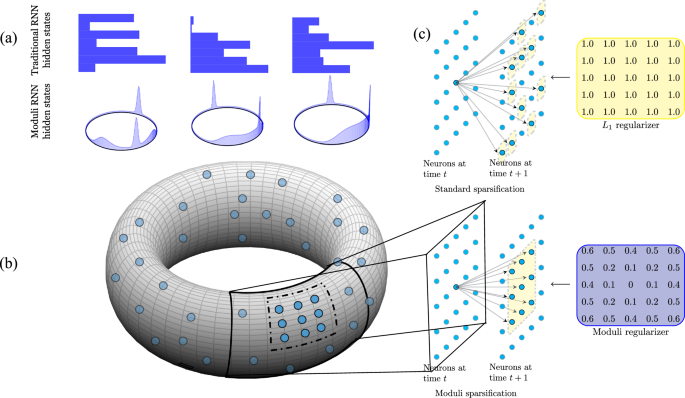
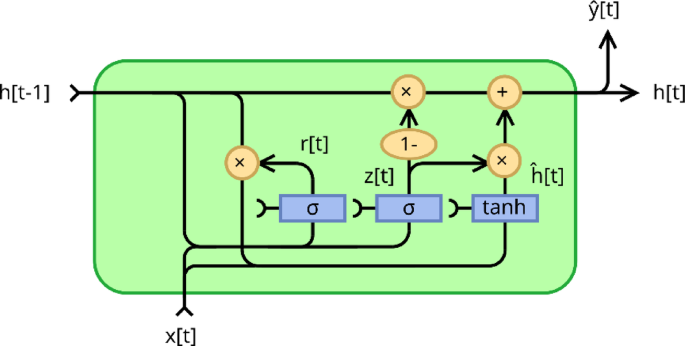
Geometric sparsification in recurrent neural networks
Theory
A recurrent neural net is a general term for any neural net designed to analyze sequences or streams of data, one element at a time. The Elman Recurrent Neural Network11, henceforward abbreviated as RNN, is a particularly simple design,…
Continue Reading
-
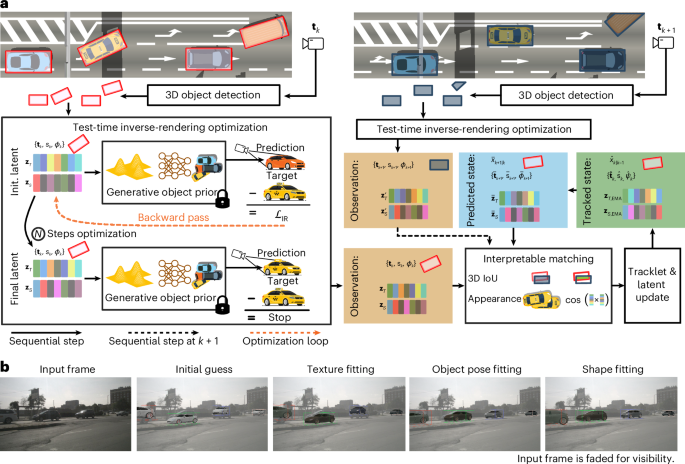
Towards generalizable and interpretable three-dimensional tracking with inverse neural rendering
Overview
In this work, we leverage inverse rendering and generative object priors to infer and track 3D multi-object scenes by jointly optimizing object pose, geometry and appearance. Our approach focuses on scenarios where an accurate scene…
Continue Reading