Fava M, Kendler KS. Major depressive disorder. Neuron. 2000;28:335–41.
Google Scholar
Owen MJ, Sawa A, Mortensen PB. Schizophrenia. Lancet. 2016;388:86–97.
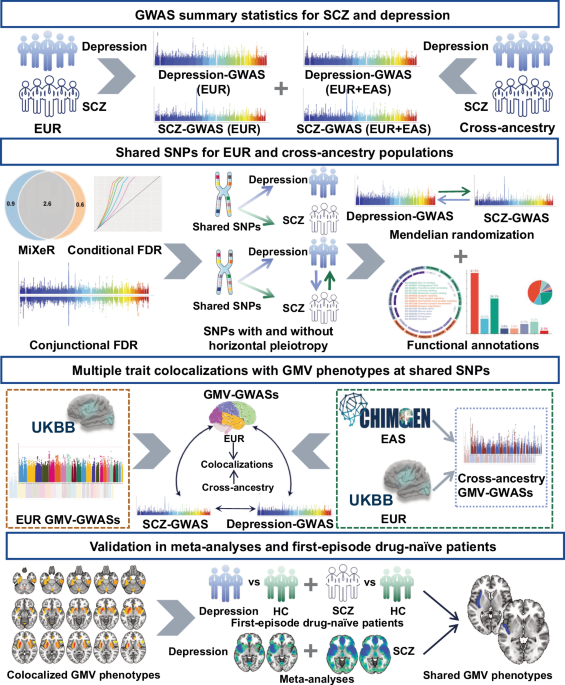
Fava M, Kendler KS. Major depressive disorder. Neuron. 2000;28:335–41.
Google Scholar
Owen MJ, Sawa A, Mortensen PB. Schizophrenia. Lancet. 2016;388:86–97.
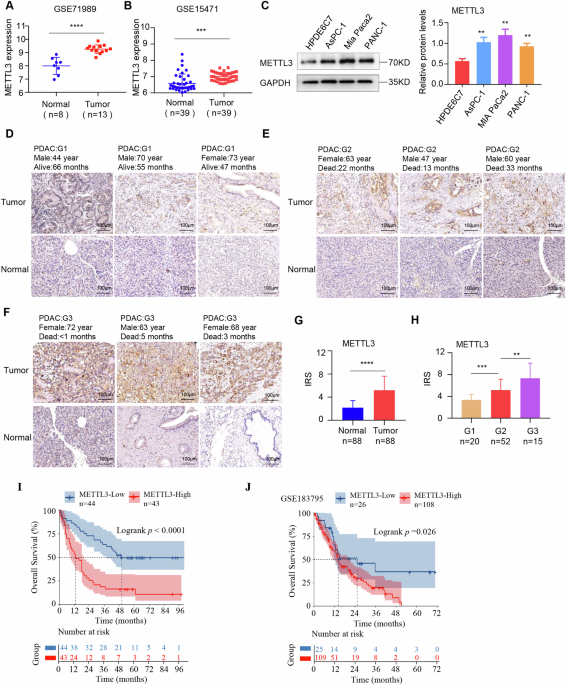
The cells utilized in this study were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA), unless otherwise indicated. HPDE6C7 and AsPC-1 cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium (Gibco, NY, USA), while…
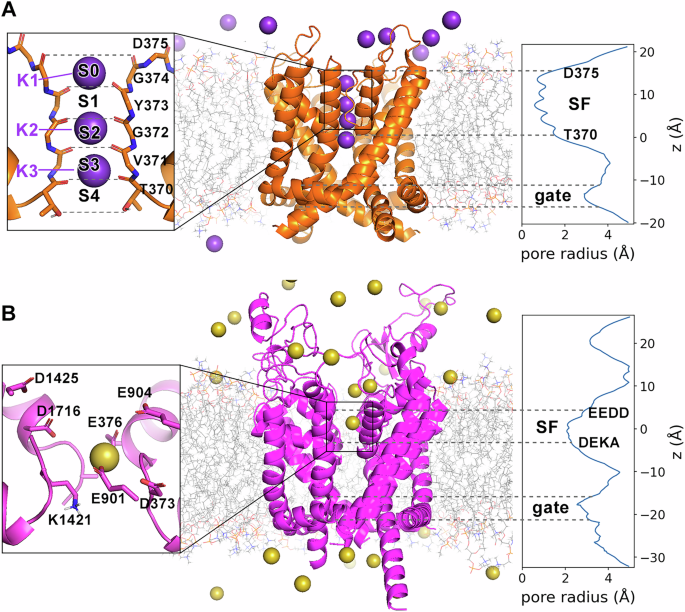
We first computed the pore radius of each ion channel using HOLE46 after equilibration to confirm that they adopt a stably open state (Fig. 1 right panels). The pore radius of Kv1.2 was 0.60 Å at SF and 2.90 Å at the…
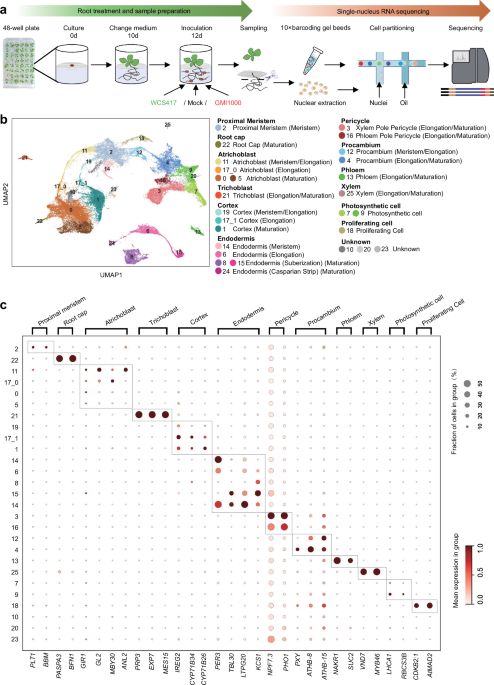
Here, we employed a 48-well plate-based hydroponic root-microbe interaction system4,21 to segregate roots and leaves using a mesh and maintain…
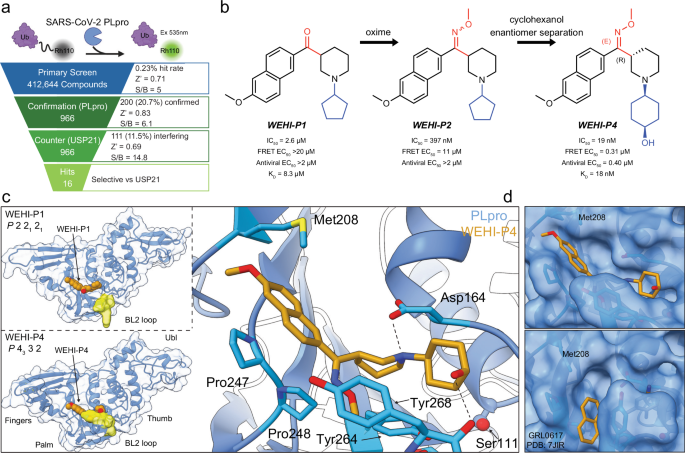
Ubiquitin Rhodamine110 (UbRh, UbiQ Bio, UbiQ-002), isopropyl ß-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG, Gold-Bio #I2481C100), β-mercaptoethanol (Sigma M3148), imidazole (Sigma 56749), lysozyme…
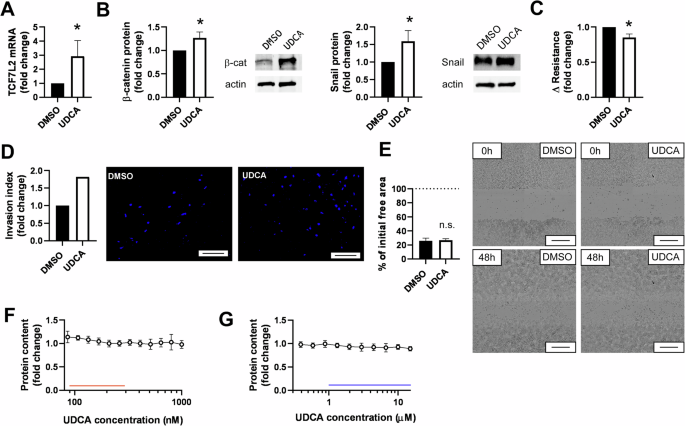
Torre LA, Trabert B, DeSantis CE, Miller KD, Samimi G, Runowicz CD, et al. Ovarian cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:284–96.
Google Scholar
Colombo N, Sessa C,…
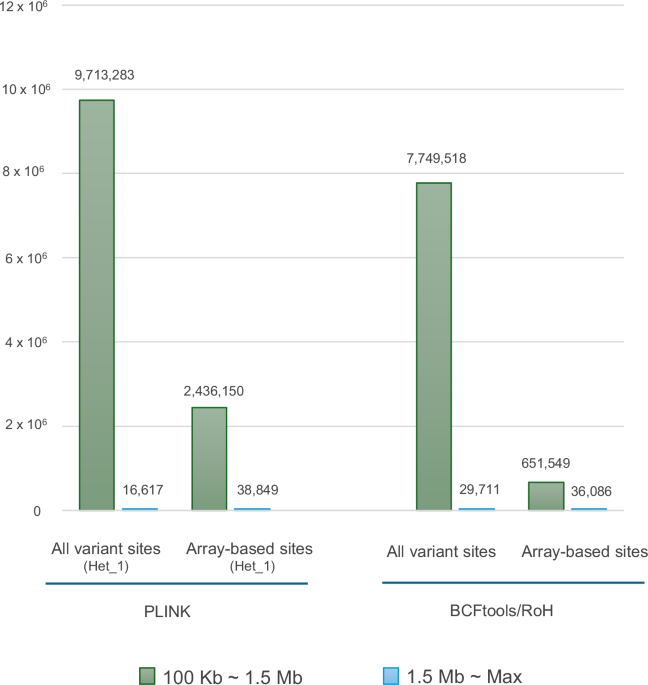
Profiling of runs of homozygosity from whole-genome sequence data in Japanese biobank
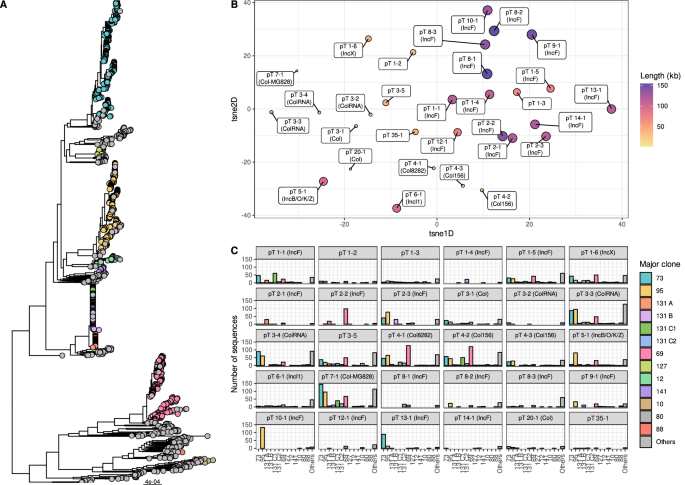
Donnenberg, M. Escherichia Coli: Pathotypes and Principles of Pathogenesis (Academic Press, 2013).
Massot, M. et al. Phylogenetic, virulence and antibiotic resistance characteristics of commensal strain populations of Escherichia coli from…
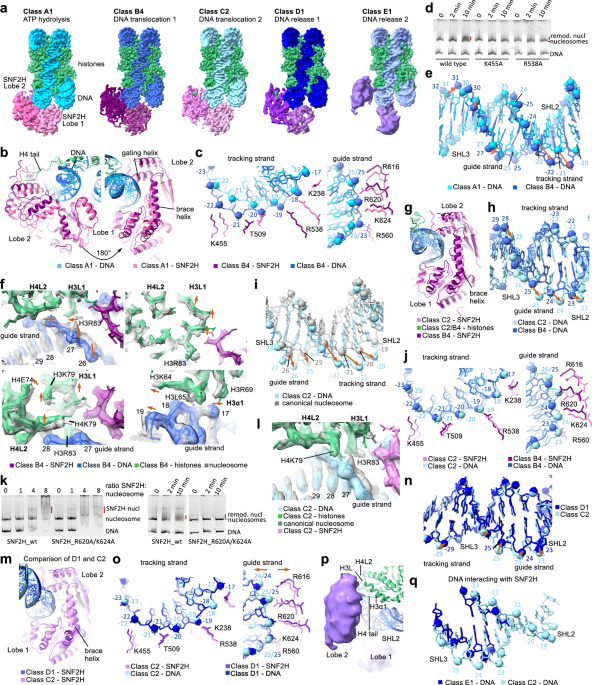
Chromatin remodelers play a crucial role in the organization of chromatin. All known remodeler enzymes use an Snf2-type ATPase motor to slide nucleosomal DNA around the histone octamer,1,2 but the…