A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on March 18, 2025, in Volume 17, Issue 3, titled “Mitochondrial oxidative stress or decreased autophagy in osteoblast lineage cells is not sufficient to mimic the deleterious…
Category: 5. Biology
-
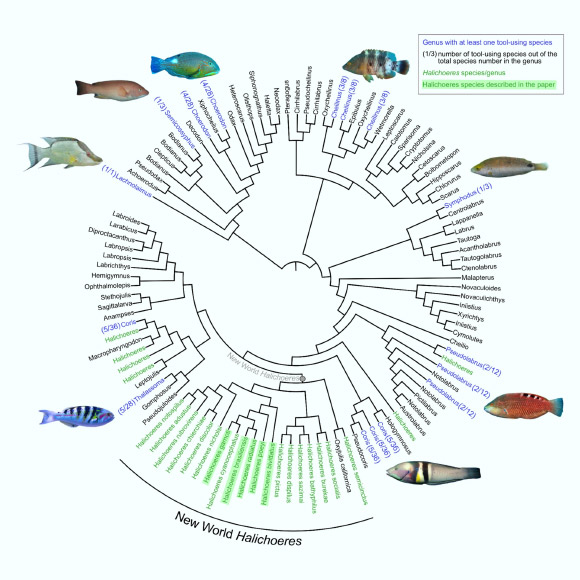
Tool Use Observed in Multiple Species of Wrasses
A diverse array of animals has evolved the ability to use tools (e.g., primates, parrots, octopus, crabs, and wasps), but the factors leading to tool use evolution are poorly understood. Fishes could provide insight into these factors via…
Continue Reading
-

Novel computational tool helps scientists detect hidden cell types behind disease
Cells throughout the body work together like singers in a choir to keep us healthy, as long as they work in perfect harmony. If any cells are off key, that harmony can be disrupted, with far-reaching effects across the body. By…
Continue Reading
-
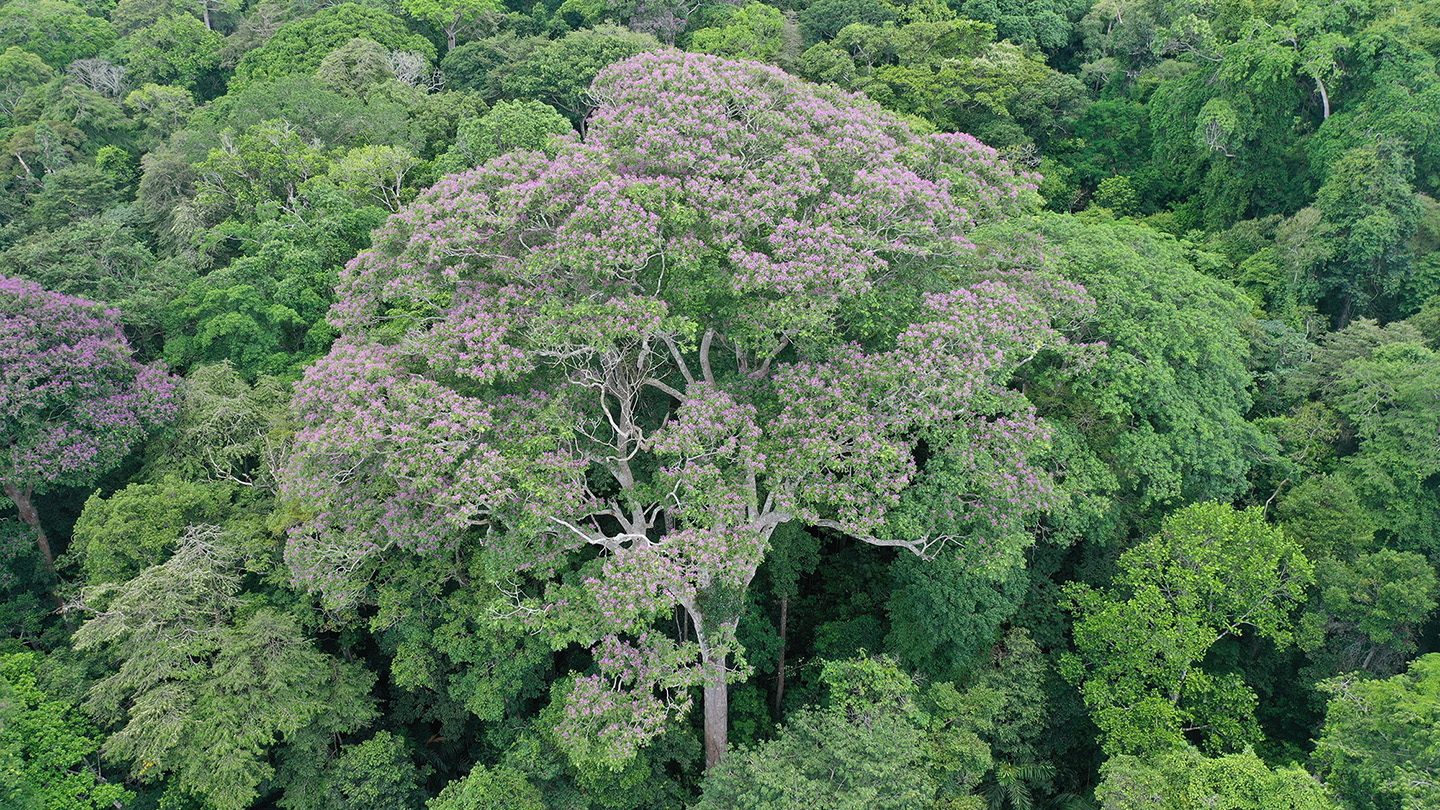

Some tropical trees act as lightning rods to fend off rivals
Getting hit by lightning is not usually a good thing. But one tropical tree species seems to harness heaven’s wrath. Not only do the trees survive lightning strikes, but their height and voluminous crowns act as natural lightning…
Continue Reading
-
X vs. Y: The Hidden Genetic War That Decides Sex
Deep within the cells of mice, a genetic arms race is unfolding between X and Y chromosome genes, battling for dominance in sperm. Researchers have now discovered how these gene families compete by hijacking key proteins to boost the odds of…
Continue Reading
-

One-third of Australia’s coastal terrestrial aquaculture at risk from sea level rise by 2100
New research led by Griffith University has highlighted more than 43% of Queensland’s current productive aquaculture sites are expected to be impacted by sea level rise.
Of the projected inundation caused by sea level rise, it is estimated 98 per…
Continue Reading
-

The lush past of the world’s largest desert
The Empty Quarter (Rub’ al-Khali), the vast desert of the Arabian Peninsula, was not always an arid landscape. A recent study by the University of Geneva (UNIGE), King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) in Saudi Arabia,…
Continue Reading
-

Researchers discover way to predict treatment success for parasitic skin disease
Nearly one million people worldwide are plagued annually by cutaneous leishmaniasis, a devastating skin infection caused by the Leishmania parasite. Predominantly affecting vulnerable populations in tropical and subtropical regions like North…
Continue Reading
-
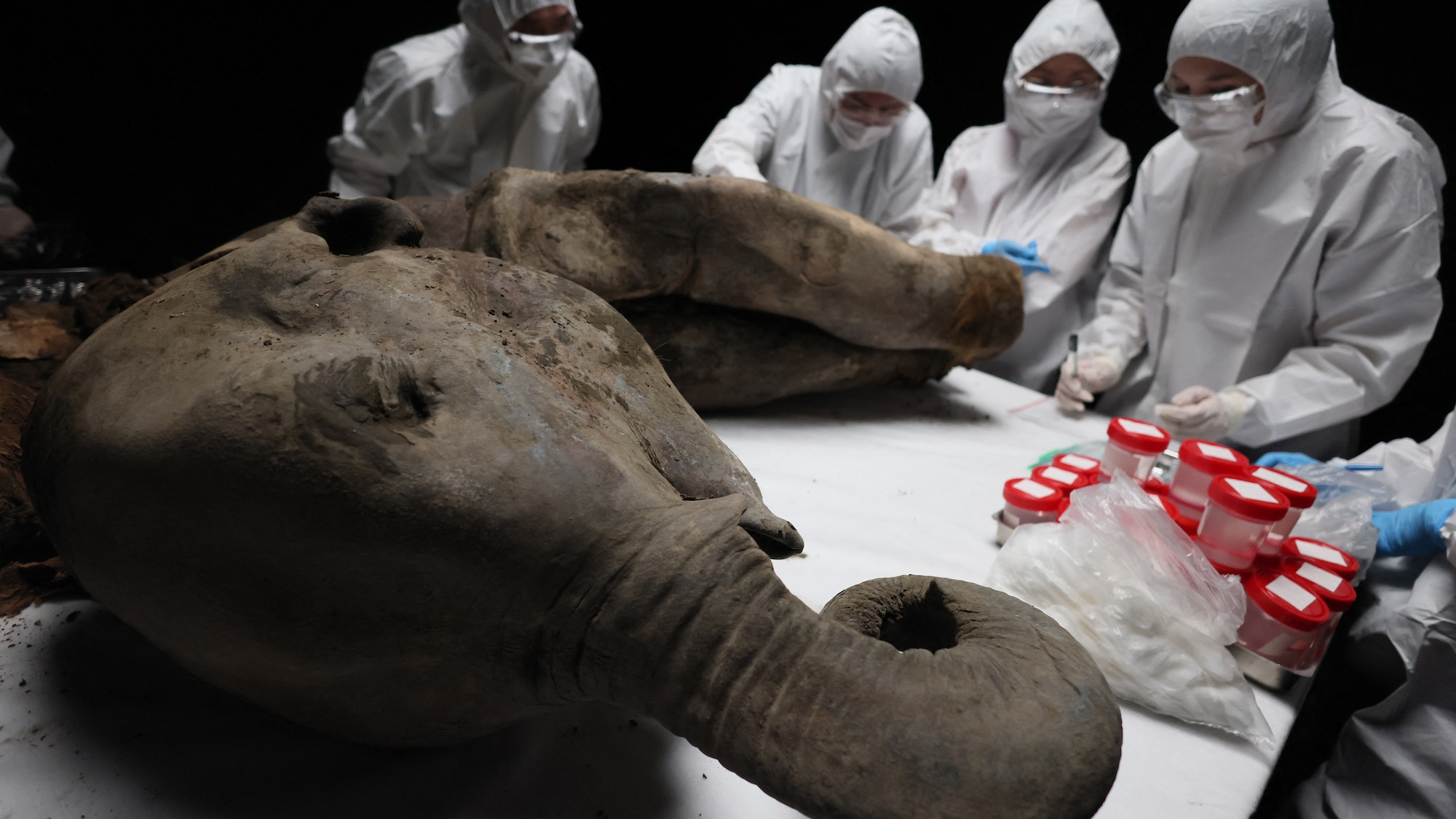

Dissected mammoth calf smells like ‘fermented earth and flesh’
A woolly mammoth calf discovered in 2024 underwent its first detailed postmortem analysis by researchers from Russia’s Institute of Experimental…
Continue Reading
-

When you were conceived could impact your weight
Global rates of metabolic disorders have been rising for decades. High blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity, and diabetes have all become much more…
Continue Reading
