Staunton, J. & Wilkinson, B. Biosynthesis of erythromycin and rapamycin. Chem. Rev. 97, 2611–2629 (1997).
Google Scholar
Floss, H. G. & Yu, T. W. Rifamycin – mode of action,…
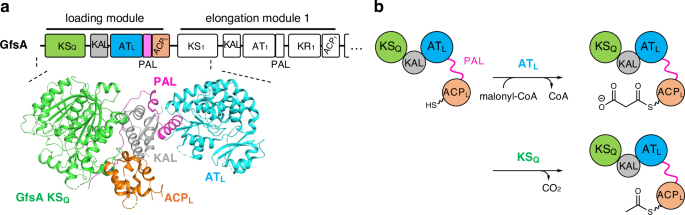
Staunton, J. & Wilkinson, B. Biosynthesis of erythromycin and rapamycin. Chem. Rev. 97, 2611–2629 (1997).
Google Scholar
Floss, H. G. & Yu, T. W. Rifamycin – mode of action,…
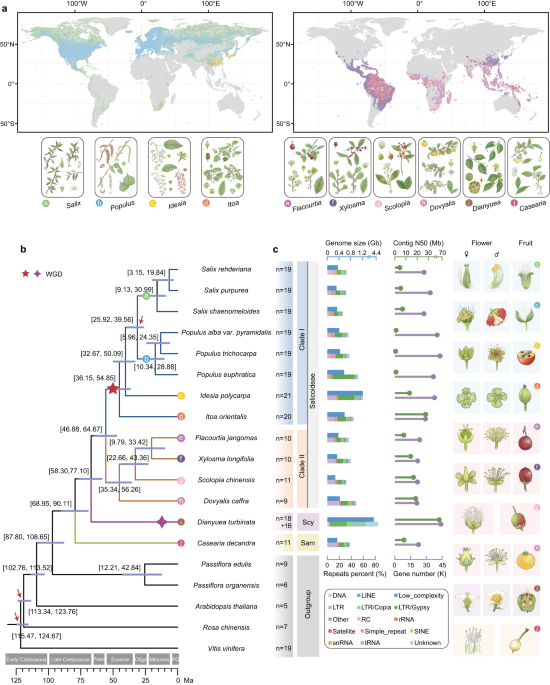
Leebens-Mack, J. H. et al. One thousand plant transcriptomes and the phylogenomics of green plants. Nature 574, 679–685 (2019).
Jiao, Y. et al. Phylogenomic analysis reveals ancient genome…
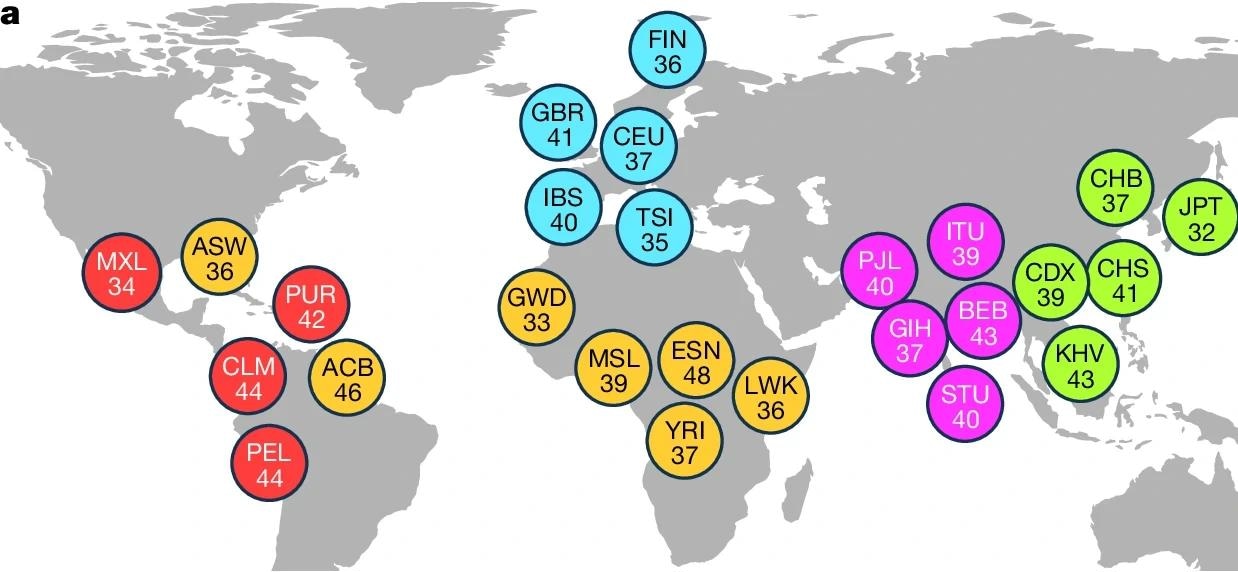
A landmark study harnesses long-read sequencing to reveal vast, previously undetected structural variations in human DNA, reshaping our understanding of genetics and disease potential.
Study: Structural variation in 1,019…

Scientists with the Wildlife Conservation Society have documented a remarkable diversity of wildlife visiting the artificial watering holes in Guatemala’s Maya Forest.
Jaguars get relief from the heat at an artificial waterhole in Guatemala….
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) and liposomes (Figure 1) have revolutionized the medical field by serving as carriers for a wide range of therapeutic molecules,
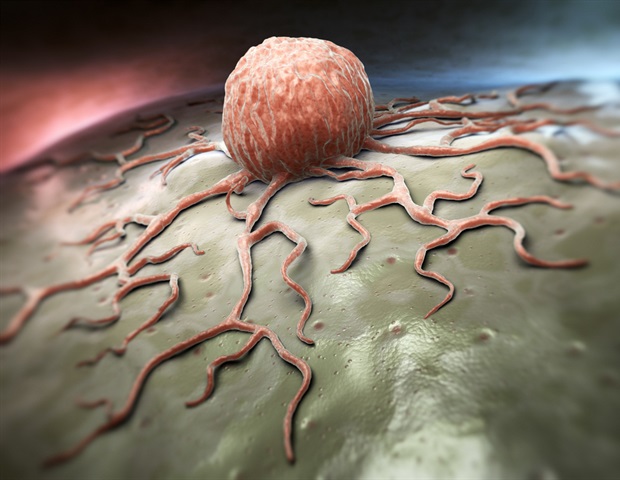
Cancer cells and tumors do not exist in a vacuum. Far from the isolation and self-sufficiency of the fictional Wakanda, tumors develop in and alter the nearby milieu of immune cells, connective tissue, blood vessels and a sea of…
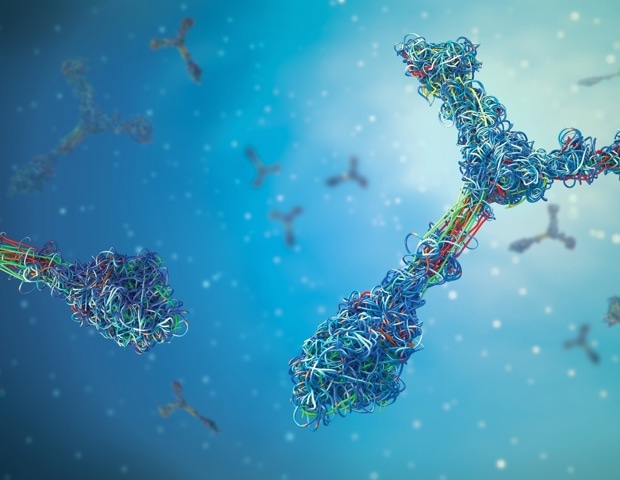
In fighting chronic infections or certain cancers, CD8+ T cells-the immune system’s frontline soldiers-eventually become exhausted. They lose effectiveness and respond less efficiently to threats. This weakening is a major…

AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) plays a central role in maintaining energy balance in cells, especially under energy stress. While upstream activation by the kinase LKB1 is well recognized, the precise mechanism by which LKB1 is…
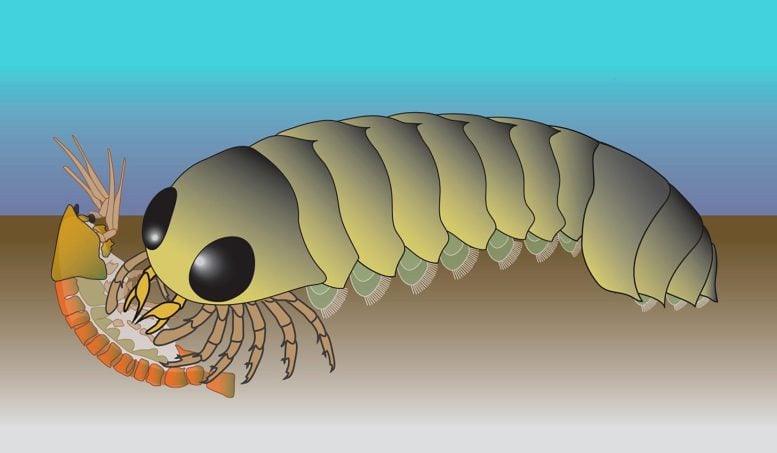
An exquisitely preserved fossil from half a billion years ago has turned our understanding of spider evolution upside down. Scientists studying the fossilized brain of Mollisonia symmetrica, a marine creature from the Cambrian period, have found…

For years, scientists thought certain parts of our DNA were useless—leftovers from ancient viruses that served no purpose. But a new international study has flipped that idea on its head. Researchers have discovered that these so-called…