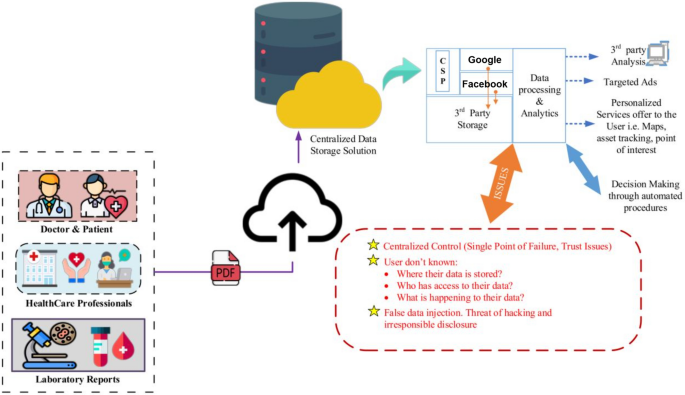
In our proposed EHRChain model, four primary entities collaborate to ensure secure and efficient electronic health record management: the blockchain, the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS), the medical system (comprising doctors and smart…
Author: admin
-
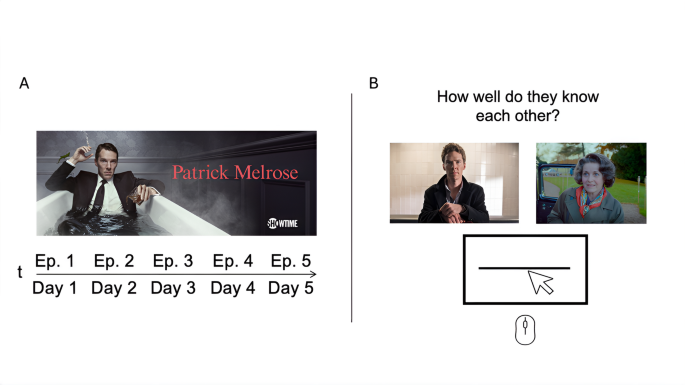
Clinician perspectives on explainability in AI-driven closed-loop neurotechnology
Qualitative results
Our qualitative analysis reveals a nuanced landscape of clinicians’ attitudes, informational needs and preferences concerning AI-driven closed-loop medical neurotechnology. To structure our findings, we organized clinician…
Continue Reading
-
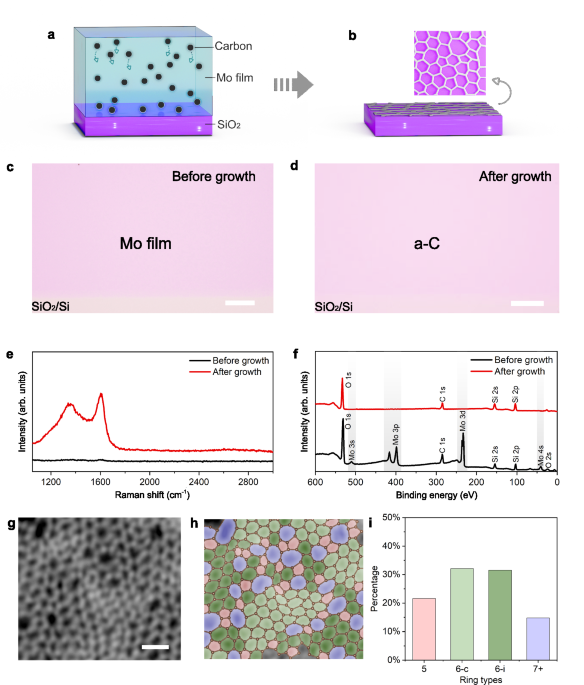
Tellurium-assisted growth of large-scale atom-thin insulating amorphous carbon on insulating substrates
Synthesis and characterization of 2D a-C
The process of synthesizing monolayer a-C film using a carbon-doped molybdenum (C-Mo) film is illustrated schematically in Fig. 1a–b. First, a C-Mo film with a thickness of ~2 nm was deposited on the…
Continue Reading
-
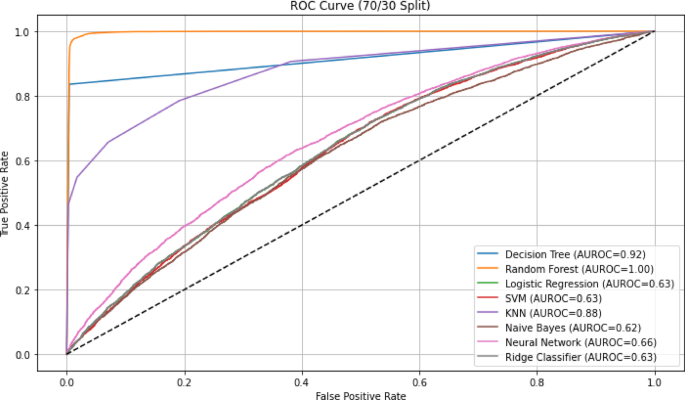
Application of machine learning models for predicting depression among older adults with non-communicable diseases in India
Table 1 illustrates both univariate and multivariable logistic regression analyses presenting the unadjusted odds ratio, adjusted odds ratio, 95% confidence interval (CI) and p-value for various factors associated with self-reported depression…
Continue Reading
-

Opinionated science | Nature Chemistry
Palmer, J. Nature 625, 205–206 (2024).
Google Scholar
Parks, P. & Takahashi, B. Sci. Commun. 38, 275–302 (2016).
Google Scholar
…Continue Reading
-
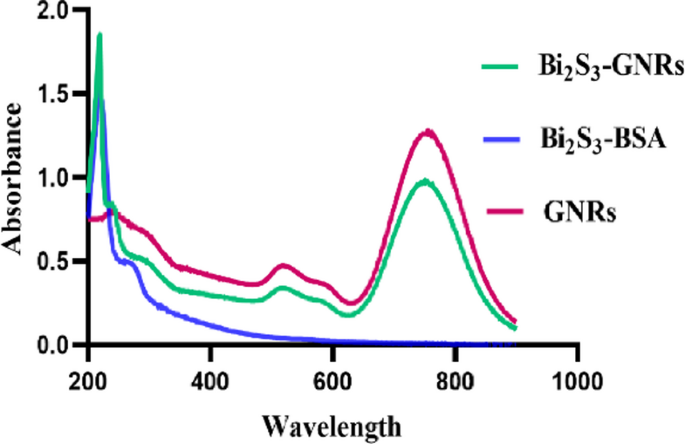
Photothermal therapy and radiotherapy of Bi2S3-GNRs hybrid nanoparticles in treatment of breast cancer
Materials
Bismuth (III) nitrate pentahydrate (Bi(NO3)3), bovine serum albumin (BSA), ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide (EDC) and phosphate buffer saline (PBS) were purchased from Sigma Aldrich, USA, Nitric acid (HNO3), silver nitrate…
Continue Reading
-
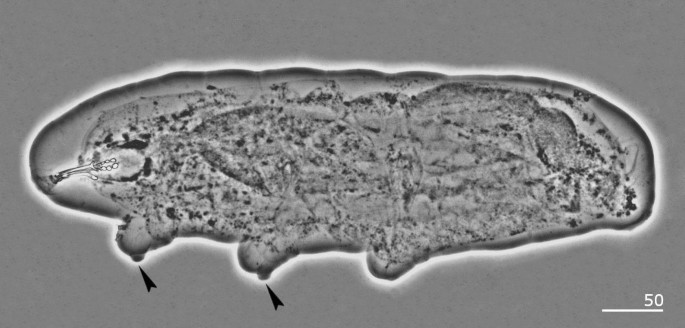
Integrative taxonomy elucidates phylogenetic position of a clawless African eutardigrade (Tardigrada) supporting the erection of a new genus
Doyère, L. M. F. Mémoire Sur les tardigrades. Ann Sci. Nat Paris Série 2. 14, 269–362 (1840).
Keiijn, D. The problem of anabiosis or latent life: history and current concepts. Proc. R Soc.…
Continue Reading
-
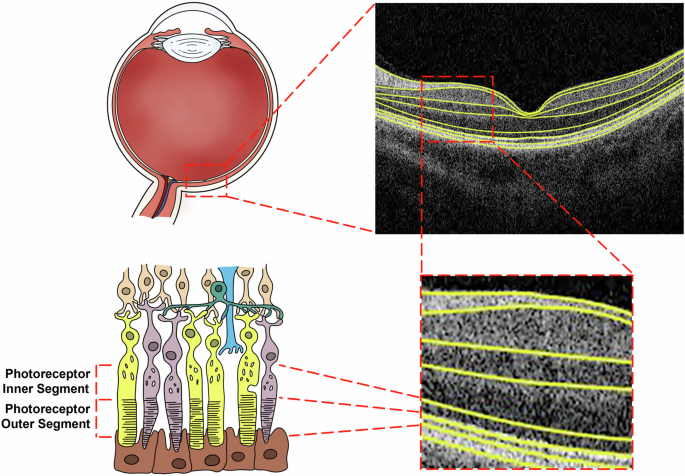
Photoreceptor layer thinning is an early biomarker for type 2 diabetes: a cohort study in UK Biobank
Skyler JS, Bakris GL, Bonifacio E, Darsow T, Eckel RH, Groop L, et al. Differentiation of diabetes by pathophysiology, natural history, and prognosis. Diabetes. 2017;66:241–55.
Google…
Continue Reading
-
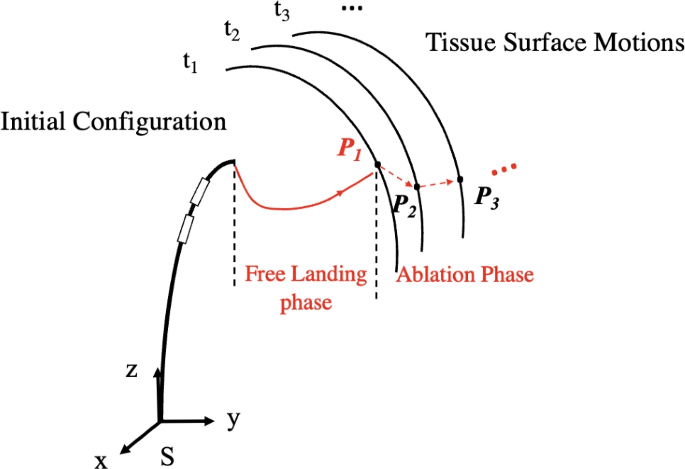
Landing control of a magnetically actuated robotic catheter on beating heart surface
In this section, we investigate the optimal landing strategy to establish a stable tip-tissue contact with appropriate ablation force for the MRI-actuated robotic catheter ablation. The ablation phase analysis is first presented, where the timing…
Continue Reading